Partially-Shared Variational Auto-encoders for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Target Shift
Paper and Code
Jan 25, 2020
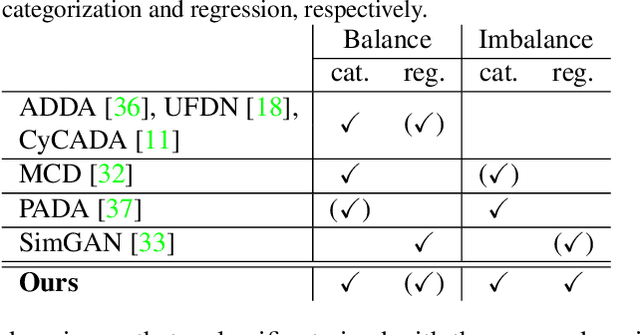


This paper proposes a novel approach for unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) with target shift. Target shift is a problem of mismatch in label distribution between source and target domains. Typically it appears as class-imbalance in target domain. In practice, this is an important problem in UDA; as we do not know labels in target domain datasets, we do not know whether or not its distribution is identical to that in the source domain dataset. Many traditional approaches achieve UDA with distribution matching by minimizing mean maximum discrepancy or adversarial training; however these approaches implicitly assume a coincidence in the distributions and do not work under situations with target shift. Some recent UDA approaches focus on class boundary and some of them are robust to target shift, but they are only applicable to classification and not to regression. To overcome the target shift problem in UDA, the proposed method, partially shared variational autoencoders (PS-VAEs), uses pair-wise feature alignment instead of feature distribution matching. PS-VAEs inter-convert domain of each sample by a CycleGAN-based architecture while preserving its label-related content. To evaluate the performance of PS-VAEs, we carried out two experiments: UDA with class-unbalanced digits datasets (classification), and UDA from synthesized data to real observation in human-pose-estimation (regression). The proposed method presented its robustness against the class-imbalance in the classification task, and outperformed the other methods in the regression task with a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge