Pack and Detect: Fast Object Detection in Videos Using Region-of-Interest Packing
Paper and Code
Oct 01, 2018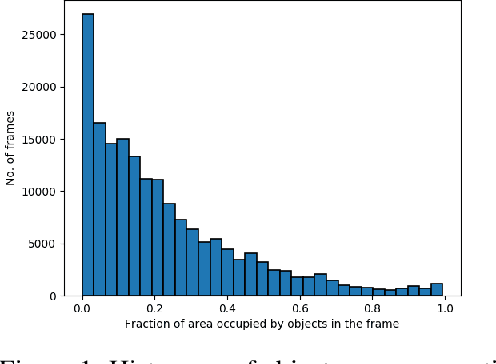
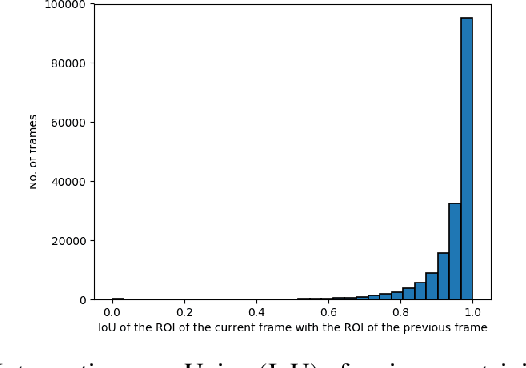
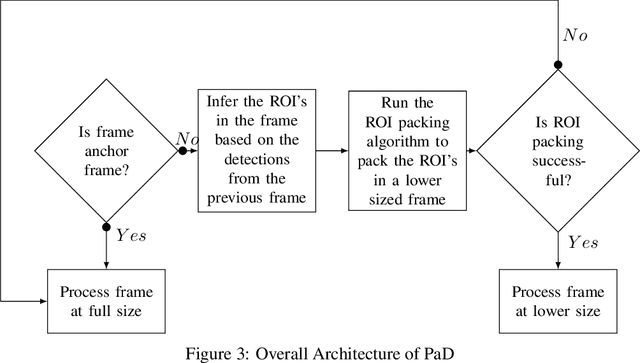
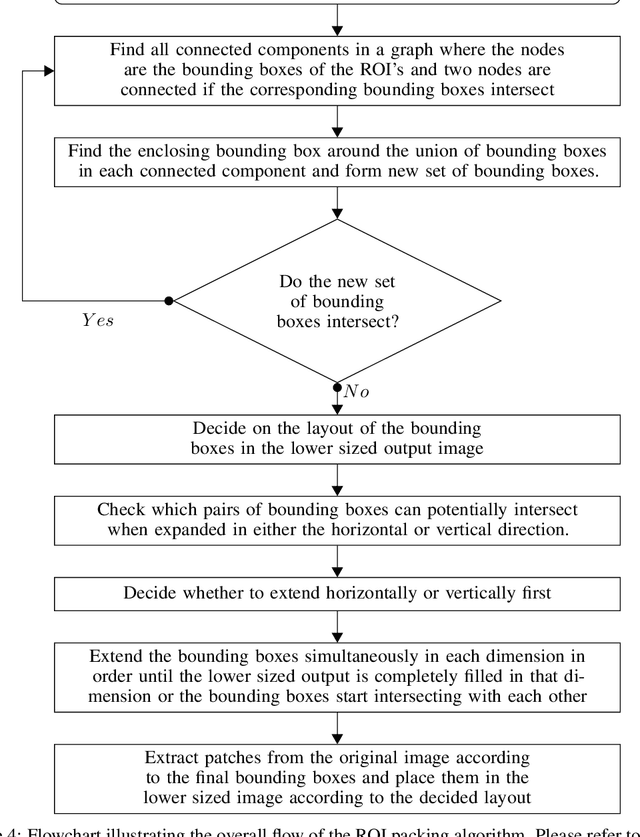
Object detection in videos is an important task in computer vision for various applications such as object tracking, video summarization and video search. Although great progress has been made in improving the accuracy of object detection in recent years due to improved techniques for training and deploying deep neural networks, they are computationally very intensive. For example, processing a video at 300x300 resolution using the SSD300 (Single Shot Detector) object detection network with VGG16 as backbone at 30 fps requires 1.87 trillion FLOPS/s. In order to address this challenge, we make two important observations in the context of videos. In some scenarios, most of the regions in a video frame are background and the salient objects occupy only a small fraction of the area in the frame. Further, in a video, there is a strong temporal correlation between consecutive frames. Based on these observations, we propose Pack and Detect (PaD) to reduce the computational requirements for the task of object detection in videos using neural networks. In PaD, the input video frame is processed at full size in selected frames called anchor frames. In the frames between the anchor frames, namely inter-anchor frames, the regions of interest(ROI) are identified based on the detections in the previous frame. We propose an algorithm to pack the ROI's of each inter-anchor frame together in a lower sized frame. In order to maintain the accuracy of object detection, the proposed algorithm expands the ROI's greedily to provide more background information to the detector. The computational requirements are reduced due to the lower size of the input. This method can potentially reduce the number of FLOPS required for a frame by 4x. Tuning the algorithm parameters can provide a 1.3x increase in throughput with only a 2.5% drop in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge