Optimal Privacy-Preserving Distributed Median Consensus
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2025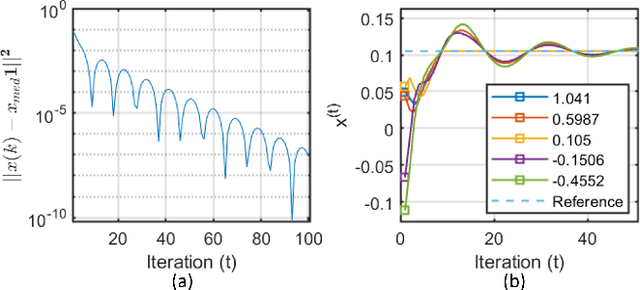
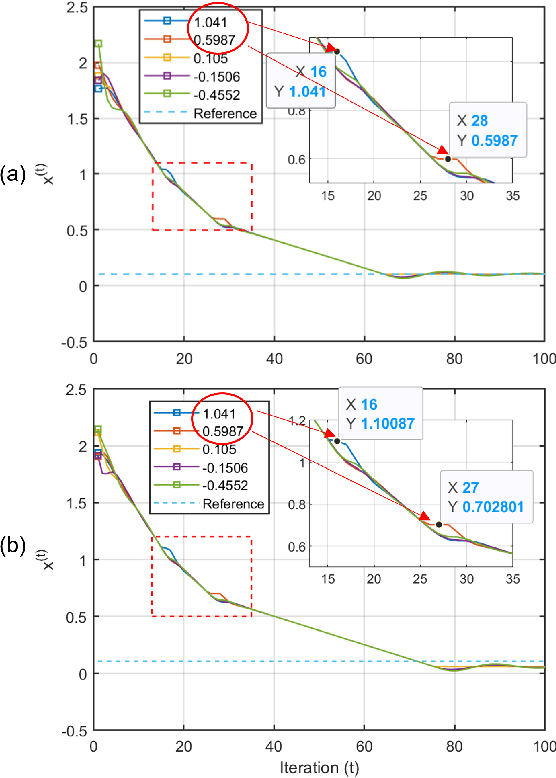
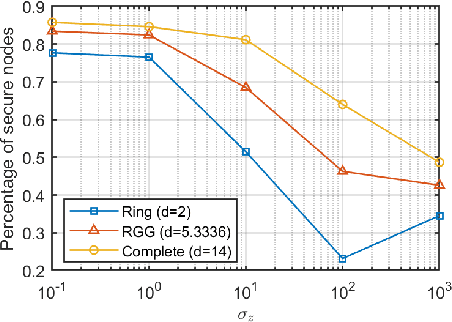
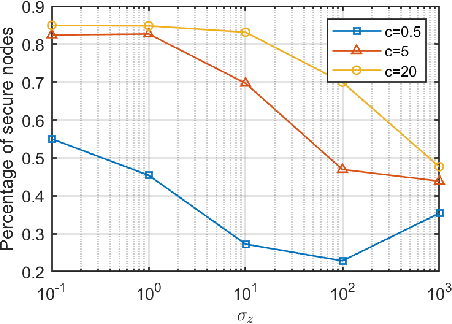
Distributed median consensus has emerged as a critical paradigm in multi-agent systems due to the inherent robustness of the median against outliers and anomalies in measurement. Despite the sensitivity of the data involved, the development of privacy-preserving mechanisms for median consensus remains underexplored. In this work, we present the first rigorous analysis of privacy in distributed median consensus, focusing on an $L_1$-norm minimization framework. We establish necessary and sufficient conditions under which exact consensus and perfect privacy-defined as zero information leakage-can be achieved simultaneously. Our information-theoretic analysis provides provable guarantees against passive and eavesdropping adversaries, ensuring that private data remain concealed. Extensive numerical experiments validate our theoretical results, demonstrating the practical feasibility of achieving both accuracy and privacy in distributed median consensus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge