Operationalizing Complex Causes: A Pragmatic View of Mediation
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2021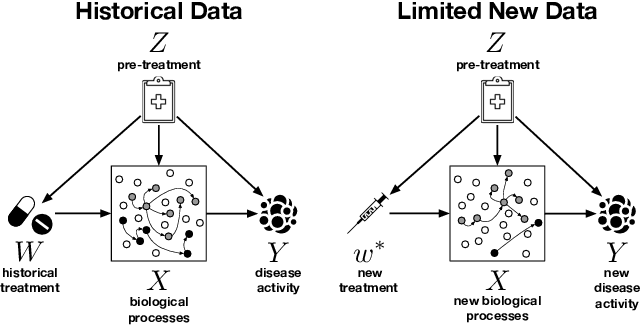

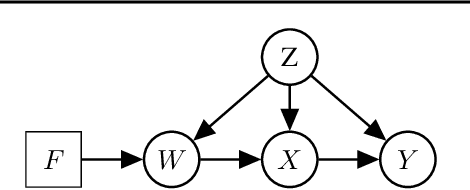
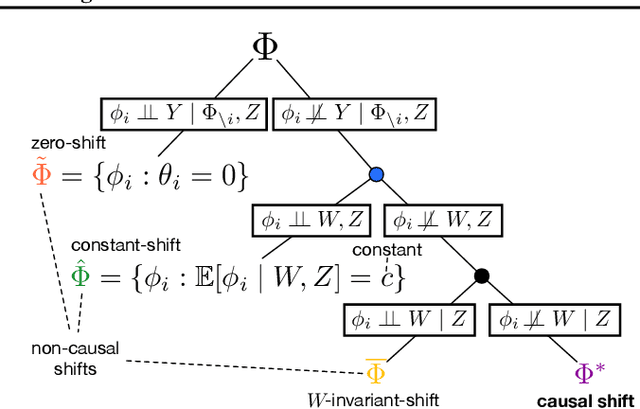
We examine the problem of causal response estimation for complex objects (e.g., text, images, genomics). In this setting, classical \emph{atomic} interventions are often not available (e.g., changes to characters, pixels, DNA base-pairs). Instead, we only have access to indirect or \emph{crude} interventions (e.g., enrolling in a writing program, modifying a scene, applying a gene therapy). In this work, we formalize this problem and provide an initial solution. Given a collection of candidate mediators, we propose (a) a two-step method for predicting the causal responses of crude interventions; and (b) a testing procedure to identify mediators of crude interventions. We demonstrate, on a range of simulated and real-world-inspired examples, that our approach allows us to efficiently estimate the effect of crude interventions with limited data from new treatment regimes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge