OpenBench: A New Benchmark and Baseline for Semantic Navigation in Smart Logistics
Paper and Code
Feb 13, 2025
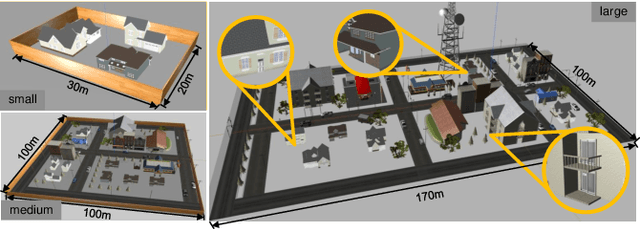

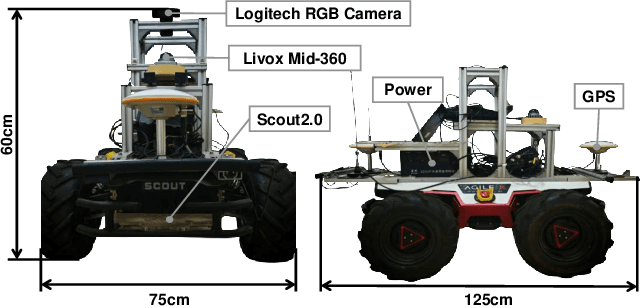
The increasing demand for efficient last-mile delivery in smart logistics underscores the role of autonomous robots in enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. Traditional navigation methods, which depend on high-precision maps, are resource-intensive, while learning-based approaches often struggle with generalization in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, this work proposes the Openstreetmap-enhanced oPen-air sEmantic Navigation (OPEN) system that combines foundation models with classic algorithms for scalable outdoor navigation. The system uses off-the-shelf OpenStreetMap (OSM) for flexible map representation, thereby eliminating the need for extensive pre-mapping efforts. It also employs Large Language Models (LLMs) to comprehend delivery instructions and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for global localization, map updates, and house number recognition. To compensate the limitations of existing benchmarks that are inadequate for assessing last-mile delivery, this work introduces a new benchmark specifically designed for outdoor navigation in residential areas, reflecting the real-world challenges faced by autonomous delivery systems. Extensive experiments in simulated and real-world environments demonstrate the proposed system's efficacy in enhancing navigation efficiency and reliability. To facilitate further research, our code and benchmark are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge