On the use of recurrent neural networks for predictions of turbulent flows
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2020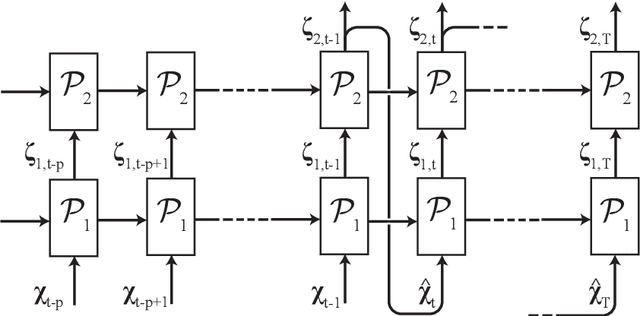
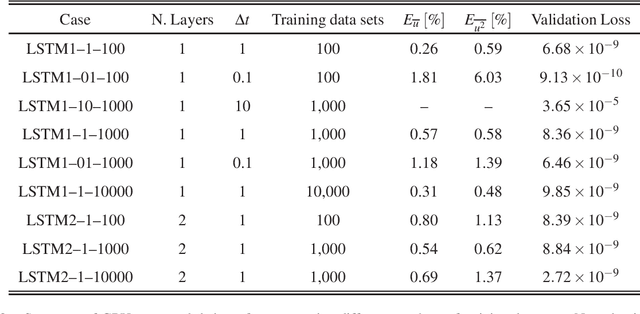
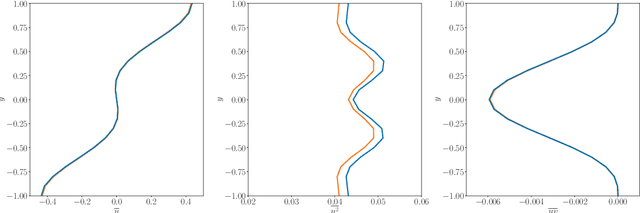

In this paper, the prediction capabilities of recurrent neural networks are assessed in the low-order model of near-wall turbulence by Moehlis {\it et al.} (New J. Phys. {\bf 6}, 56, 2004). Our results show that it is possible to obtain excellent predictions of the turbulence statistics and the dynamic behavior of the flow with properly trained long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, leading to relative errors in the mean and the fluctuations below $1\%$. We also observe that using a loss function based only on the instantaneous predictions of the flow may not lead to the best predictions in terms of turbulence statistics, and it is necessary to define a stopping criterion based on the computed statistics. Furthermore, more sophisticated loss functions, including not only the instantaneous predictions but also the averaged behavior of the flow, may lead to much faster neural network training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge