On the Use of Machine Translation-Based Approaches for Vietnamese Diacritic Restoration
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2017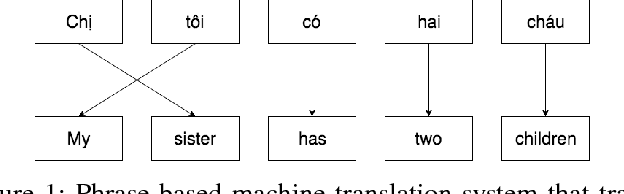
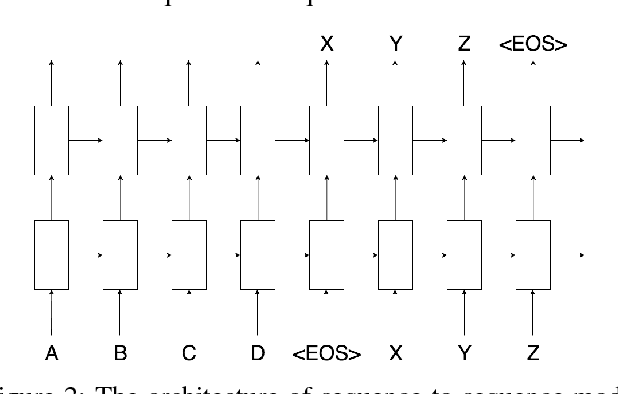
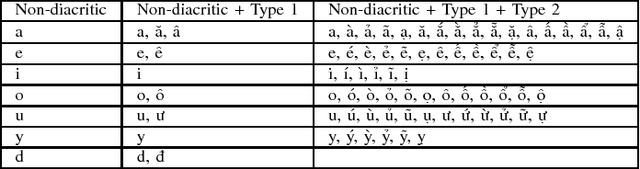
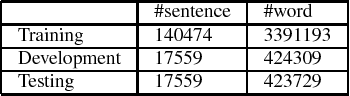
This paper presents an empirical study of two machine translation-based approaches for Vietnamese diacritic restoration problem, including phrase-based and neural-based machine translation models. This is the first work that applies neural-based machine translation method to this problem and gives a thorough comparison to the phrase-based machine translation method which is the current state-of-the-art method for this problem. On a large dataset, the phrase-based approach has an accuracy of 97.32% while that of the neural-based approach is 96.15%. While the neural-based method has a slightly lower accuracy, it is about twice faster than the phrase-based method in terms of inference speed. Moreover, neural-based machine translation method has much room for future improvement such as incorporating pre-trained word embeddings and collecting more training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge