On the Role of Field of View for Occlusion Removal with Airborne Optical Sectioning
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2022
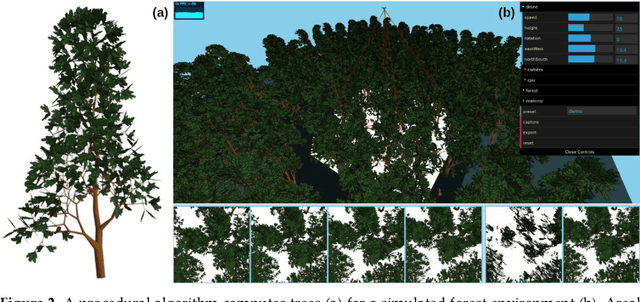
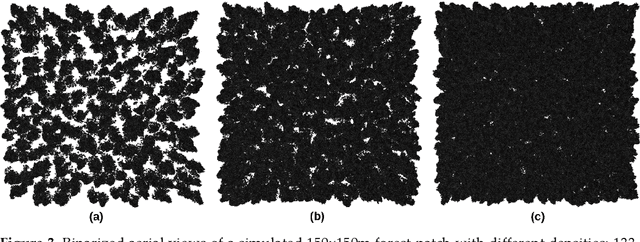
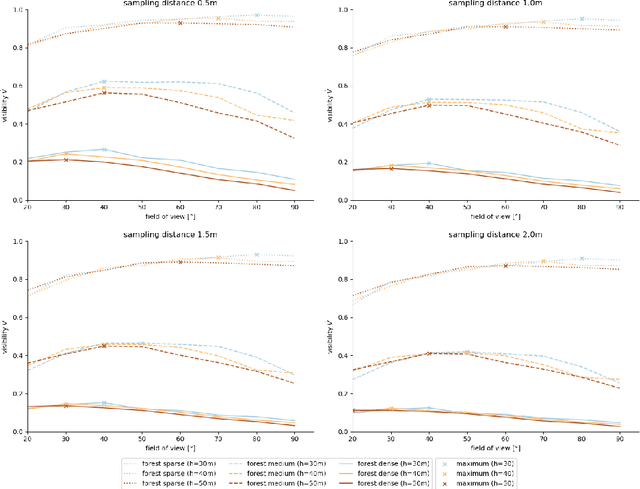
Occlusion caused by vegetation is an essential problem for remote sensing applications in areas, such as search and rescue, wildfire detection, wildlife observation, surveillance, border control, and others. Airborne Optical Sectioning (AOS) is an optical, wavelength-independent synthetic aperture imaging technique that supports computational occlusion removal in real-time. It can be applied with manned or unmanned aircrafts, such as drones. In this article, we demonstrate a relationship between forest density and field of view (FOV) of applied imaging systems. This finding was made with the help of a simulated procedural forest model which offers the consideration of more realistic occlusion properties than our previous statistical model. While AOS has been explored with automatic and autonomous research prototypes in the past, we present a free AOS integration for DJI systems. It enables bluelight organizations and others to use and explore AOS with compatible, manually operated, off-the-shelf drones. The (digitally cropped) default FOV for this implementation was chosen based on our new finding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge