On the Properties of Adversarially-Trained CNNs
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2022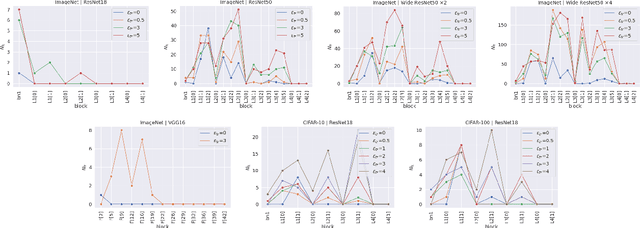
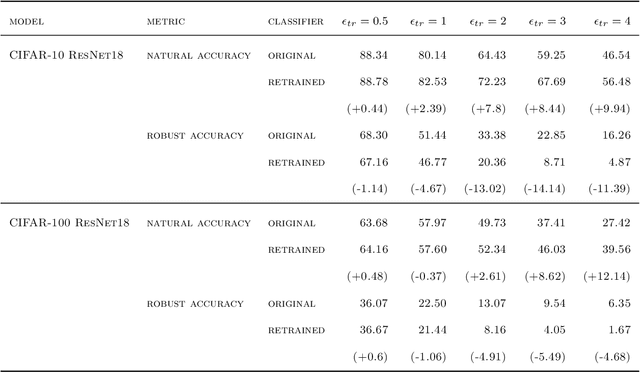
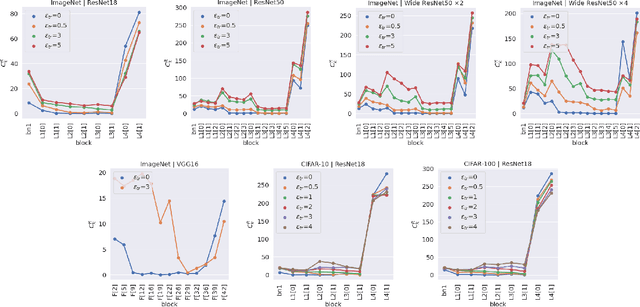

Adversarial Training has proved to be an effective training paradigm to enforce robustness against adversarial examples in modern neural network architectures. Despite many efforts, explanations of the foundational principles underpinning the effectiveness of Adversarial Training are limited and far from being widely accepted by the Deep Learning community. In this paper, we describe surprising properties of adversarially-trained models, shedding light on mechanisms through which robustness against adversarial attacks is implemented. Moreover, we highlight limitations and failure modes affecting these models that were not discussed by prior works. We conduct extensive analyses on a wide range of architectures and datasets, performing a deep comparison between robust and natural models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge