On the impact of topological properties of smart grids in power losses optimization problems
Paper and Code
Jan 21, 2015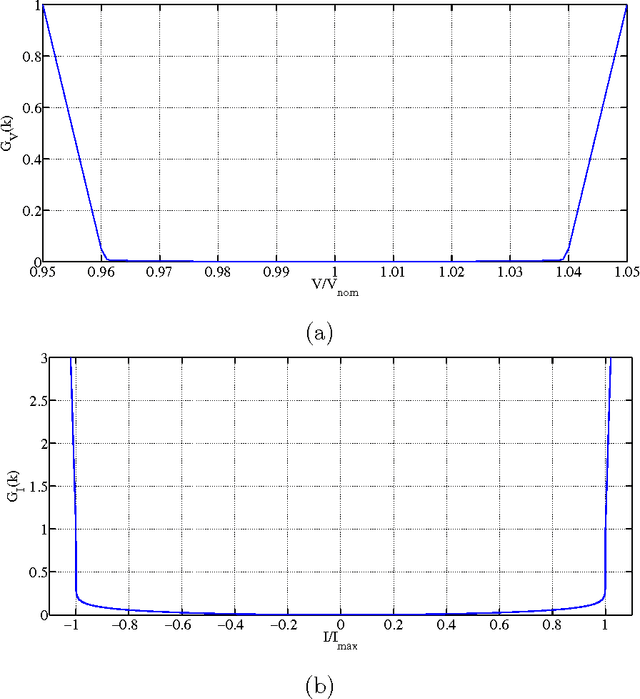
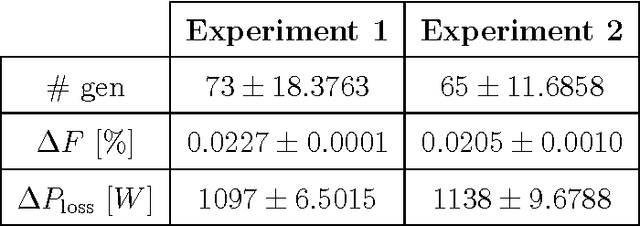
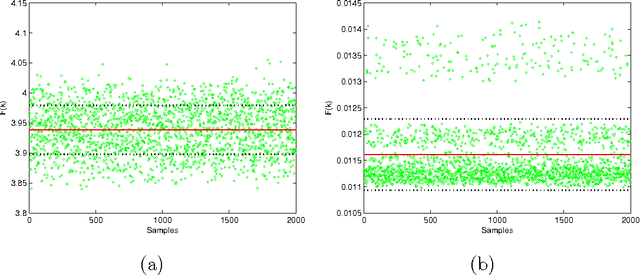
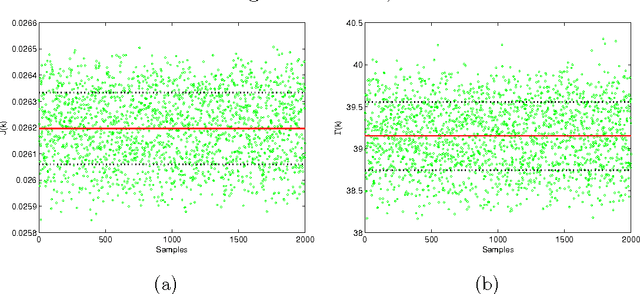
Power losses reduction is one of the main targets for any electrical energy distribution company. In this paper, we face the problem of joint optimization of both topology and network parameters in a real smart grid. We consider a portion of the Italian electric distribution network managed by the ACEA Distribuzione S.p.A. located in Rome. We perform both the power factor correction (PFC) for tuning the generators and the distributed feeder reconfiguration (DFR) to set the state of the breakers. This joint optimization problem is faced considering a suitable objective function and by adopting genetic algorithms as global optimization strategy. We analyze admissible network configurations, showing that some of these violate constraints on current and voltage at branches and nodes. Such violations depend only on pure topological properties of the configurations. We perform tests by feeding the simulation environment with real data concerning hourly samples of dissipated and generated active and reactive power values of the ACEA smart grid. Results show that removing the configurations violating the electrical constraints from the solution space leads to interesting improvements in terms of power loss reduction. To conclude, we provide also an electrical interpretation of the phenomenon using graph-based pattern analysis techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge