On the Contractivity of Plug-and-Play Operators
Paper and Code
Sep 28, 2023
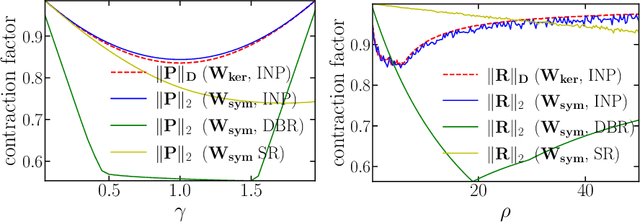
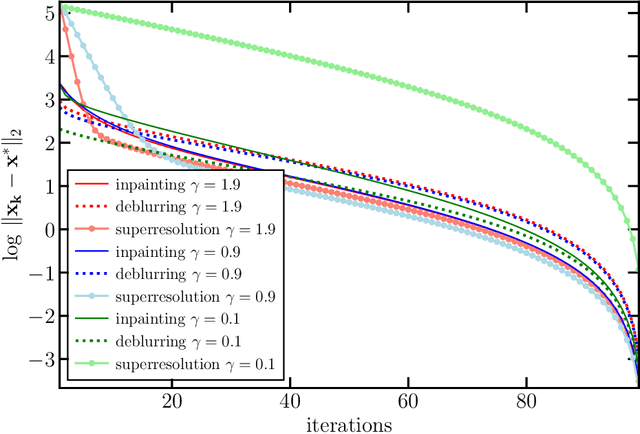

In plug-and-play (PnP) regularization, the proximal operator in algorithms such as ISTA and ADMM is replaced by a powerful denoiser. This formal substitution works surprisingly well in practice. In fact, PnP has been shown to give state-of-the-art results for various imaging applications. The empirical success of PnP has motivated researchers to understand its theoretical underpinnings and, in particular, its convergence. It was shown in prior work that for kernel denoisers such as the nonlocal means, PnP-ISTA provably converges under some strong assumptions on the forward model. The present work is motivated by the following questions: Can we relax the assumptions on the forward model? Can the convergence analysis be extended to PnP-ADMM? Can we estimate the convergence rate? In this letter, we resolve these questions using the contraction mapping theorem: (i) for symmetric denoisers, we show that (under mild conditions) PnP-ISTA and PnP-ADMM exhibit linear convergence; and (ii) for kernel denoisers, we show that PnP-ISTA and PnP-ADMM converge linearly for image inpainting. We validate our theoretical findings using reconstruction experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge