On the Context-Free Ambiguity of Emoji: A Data-Driven Study of 1,289 Emojis
Paper and Code
Jan 17, 2022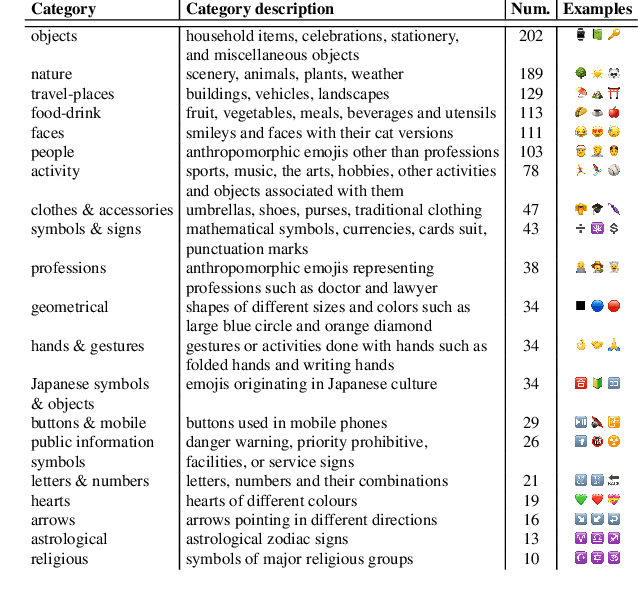
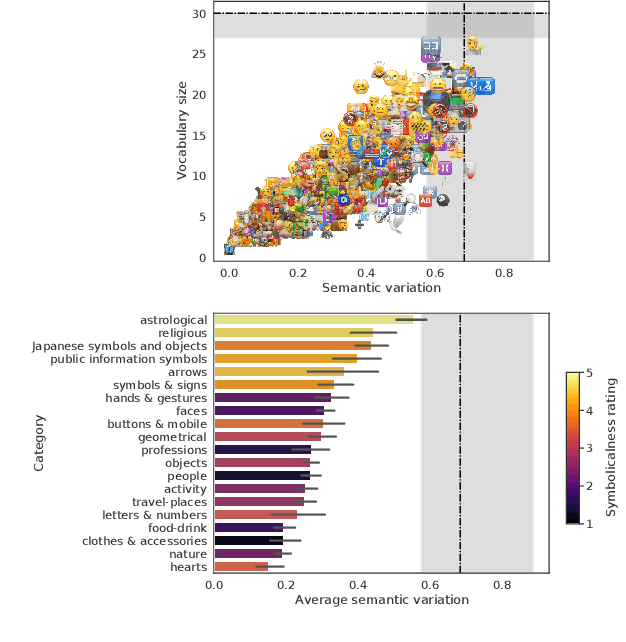
Emojis come with prepacked semantics making them great candidates to create new forms of more accessible communications. Yet, little is known about how much of this emojis semantic is agreed upon by humans, outside of textual contexts. Thus, we collected a crowdsourced dataset of one-word emoji descriptions for 1,289 emojis presented to participants with no surrounding text. The emojis and their interpretations were then examined for ambiguity. We find that with 30 annotations per emoji, 16 emojis (1.2%) are completely unambiguous, whereas 55 emojis (4.3%) are so ambiguous that their descriptions are indistinguishable from randomly chosen descriptions. Most of studied emojis are spread out between the two extremes. Furthermore, investigating the ambiguity of different types of emojis, we find that an important factor is the extent to which an emoji has an embedded symbolical meaning drawn from an established code-book of symbols. We conclude by discussing design implications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge