On the challenges of studying bias in Recommender Systems: A UserKNN case study
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2024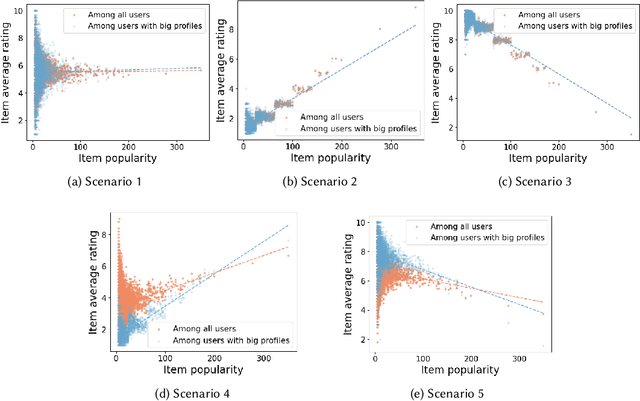

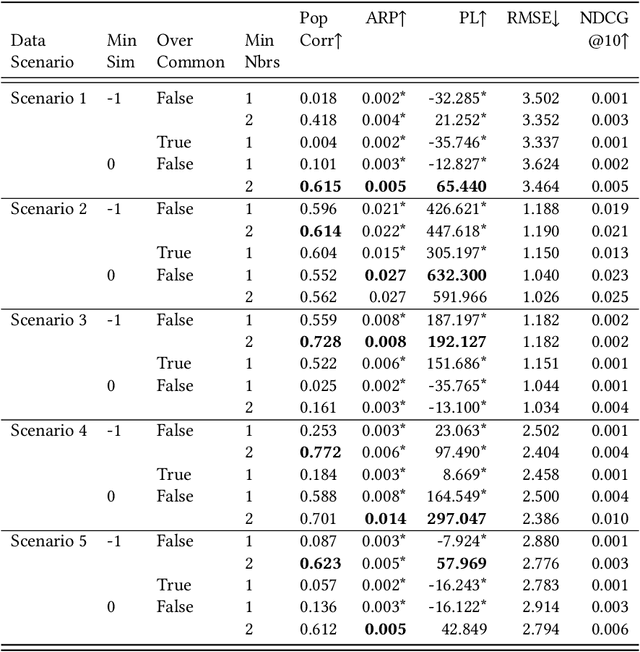
Statements on the propagation of bias by recommender systems are often hard to verify or falsify. Research on bias tends to draw from a small pool of publicly available datasets and is therefore bound by their specific properties. Additionally, implementation choices are often not explicitly described or motivated in research, while they may have an effect on bias propagation. In this paper, we explore the challenges of measuring and reporting popularity bias. We showcase the impact of data properties and algorithm configurations on popularity bias by combining synthetic data with well known recommender systems frameworks that implement UserKNN. First, we identify data characteristics that might impact popularity bias, based on the functionality of UserKNN. Accordingly, we generate various datasets that combine these characteristics. Second, we locate UserKNN configurations that vary across implementations in literature. We evaluate popularity bias for five synthetic datasets and five UserKNN configurations, and offer insights on their joint effect. We find that, depending on the data characteristics, various UserKNN configurations can lead to different conclusions regarding the propagation of popularity bias. These results motivate the need for explicitly addressing algorithmic configuration and data properties when reporting and interpreting bias in recommender systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge