On Enhancing Speech Emotion Recognition using Generative Adversarial Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2018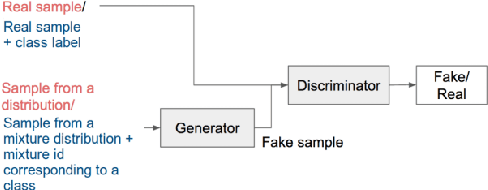
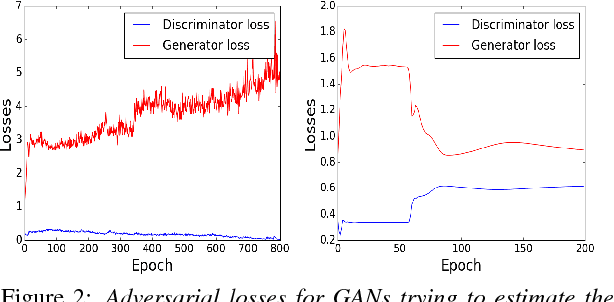
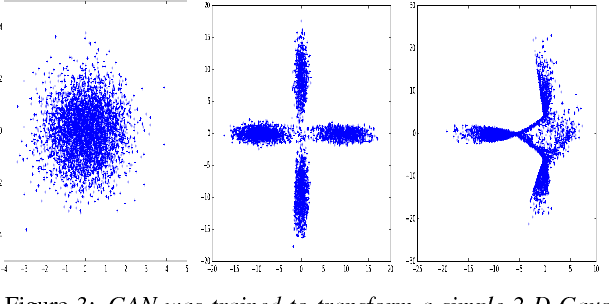
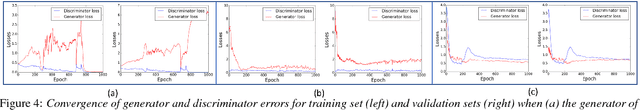
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have gained a lot of attention from machine learning community due to their ability to learn and mimic an input data distribution. GANs consist of a discriminator and a generator working in tandem playing a min-max game to learn a target underlying data distribution; when fed with data-points sampled from a simpler distribution (like uniform or Gaussian distribution). Once trained, they allow synthetic generation of examples sampled from the target distribution. We investigate the application of GANs to generate synthetic feature vectors used for speech emotion recognition. Specifically, we investigate two set ups: (i) a vanilla GAN that learns the distribution of a lower dimensional representation of the actual higher dimensional feature vector and, (ii) a conditional GAN that learns the distribution of the higher dimensional feature vectors conditioned on the labels or the emotional class to which it belongs. As a potential practical application of these synthetically generated samples, we measure any improvement in a classifier's performance when the synthetic data is used along with real data for training. We perform cross-validation analyses followed by a cross-corpus study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge