Object State Estimation Through Robotic Active Interaction for Biological Autonomous Drilling
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2025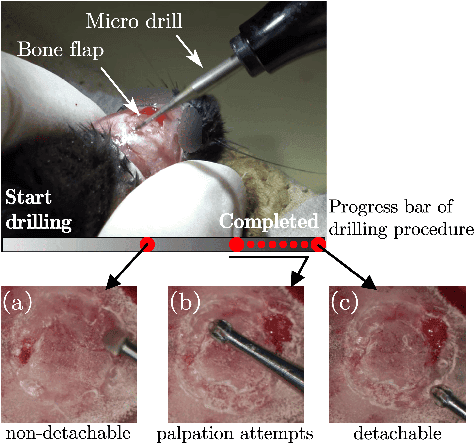
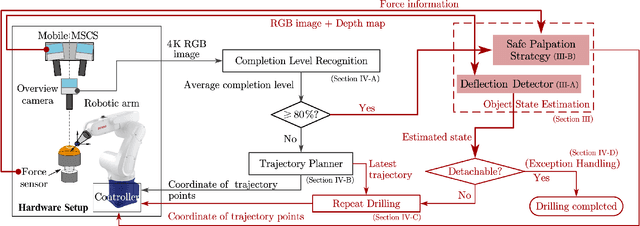
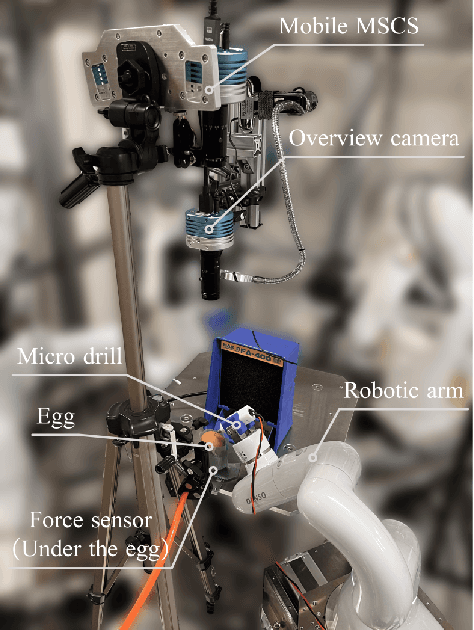
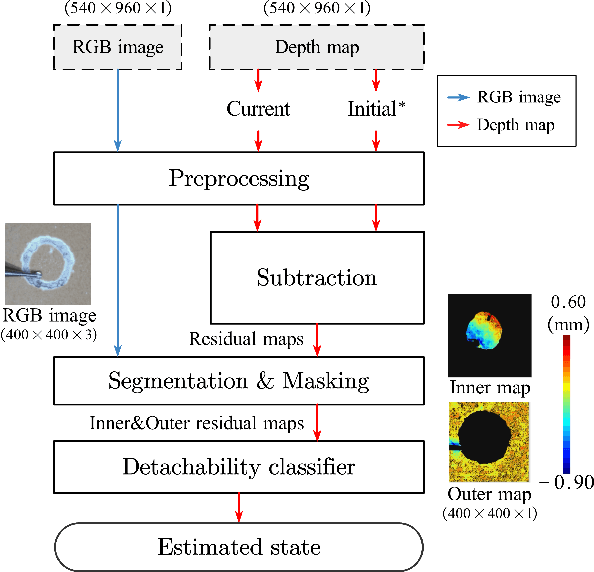
Estimating the state of biological specimens is challenging due to limited observation through microscopic vision. For instance, during mouse skull drilling, the appearance alters little when thinning bone tissue because of its semi-transparent property and the high-magnification microscopic vision. To obtain the object's state, we introduce an object state estimation method for biological specimens through active interaction based on the deflection. The method is integrated to enhance the autonomous drilling system developed in our previous work. The method and integrated system were evaluated through 12 autonomous eggshell drilling experiment trials. The results show that the system achieved a 91.7% successful ratio and 75% detachable ratio, showcasing its potential applicability in more complex surgical procedures such as mouse skull craniotomy. This research paves the way for further development of autonomous robotic systems capable of estimating the object's state through active interaction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge