Obfuscation for Privacy-preserving Syntactic Parsing
Paper and Code
Apr 21, 2019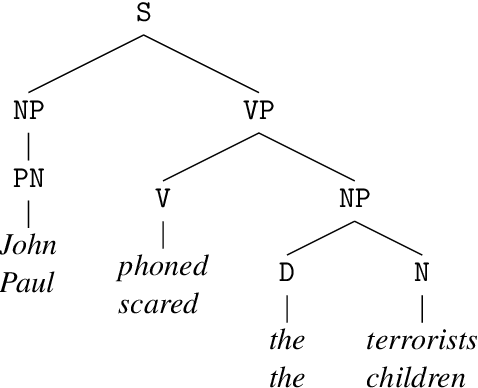
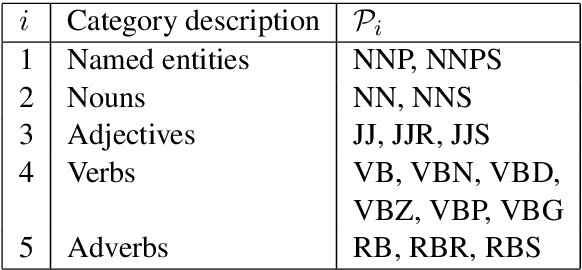
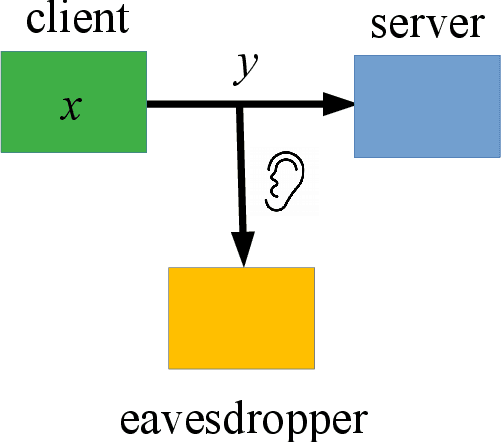
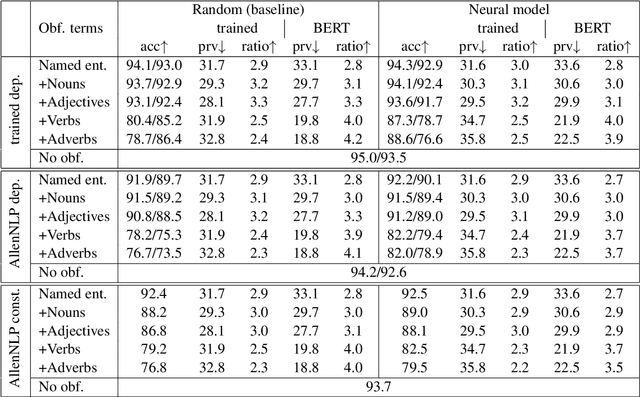
The goal of homomorphic encryption is to encrypt data such that another party can operate on it without being explicitly exposed to the content of the original data. We introduce an idea for a privacy-preserving transformation on natural language data, inspired by homomorphic encryption. Our primary tool is {\em obfuscation}, relying on the properties of natural language. Specifically, a given text is obfuscated using a neural model that aims to preserve the syntactic relationships of the original sentence so that the obfuscated sentence can be parsed instead of the original one. The model works at the word level, and learns to obfuscate each word separately by changing it into a new word that has a similar syntactic role. The text encrypted by our model leads to better performance on three syntactic parsers (two dependency and one constituency parsers) in comparison to a strong random baseline. The substituted words have similar syntactic properties, but different semantic content, compared to the original words.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge