NüshuRescue: Revitalization of the endangered Nüshu Language with AI
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2024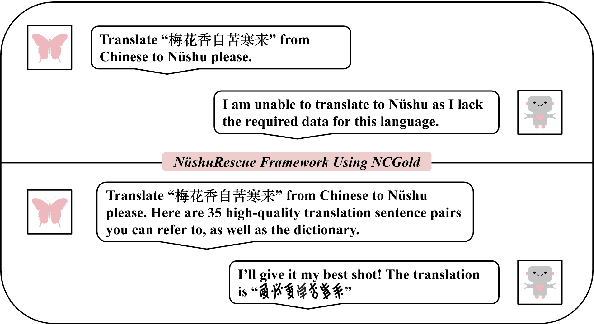
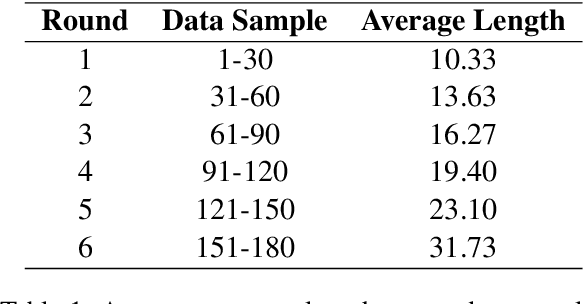

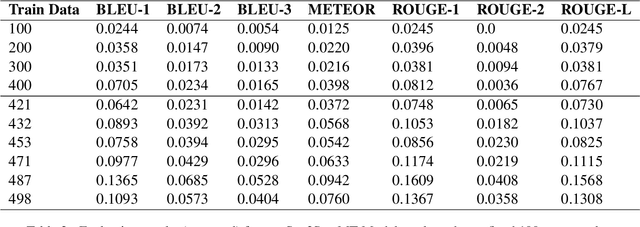
The preservation and revitalization of endangered and extinct languages is a meaningful endeavor, conserving cultural heritage while enriching fields like linguistics and anthropology. However, these languages are typically low-resource, making their reconstruction labor-intensive and costly. This challenge is exemplified by N\"ushu, a rare script historically used by Yao women in China for self-expression within a patriarchal society. To address this challenge, we introduce N\"ushuRescue, an AI-driven framework designed to train large language models (LLMs) on endangered languages with minimal data. N\"ushuRescue automates evaluation and expands target corpora to accelerate linguistic revitalization. As a foundational component, we developed NCGold, a 500-sentence N\"ushu-Chinese parallel corpus, the first publicly available dataset of its kind. Leveraging GPT-4-Turbo, with no prior exposure to N\"ushu and only 35 short examples from NCGold, N\"ushuRescue achieved 48.69\% translation accuracy on 50 withheld sentences and generated NCSilver, a set of 98 newly translated modern Chinese sentences of varying lengths. A sample of both NCGold and NCSilver is included in the Supplementary Materials. Additionally, we developed FastText-based and Seq2Seq models to further support research on N\"ushu. N\"ushuRescue provides a versatile and scalable tool for the revitalization of endangered languages, minimizing the need for extensive human input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge