Nonparametric Bayesian Sparse Graph Linear Dynamical Systems
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2018
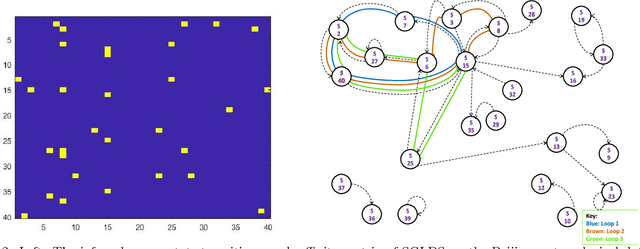

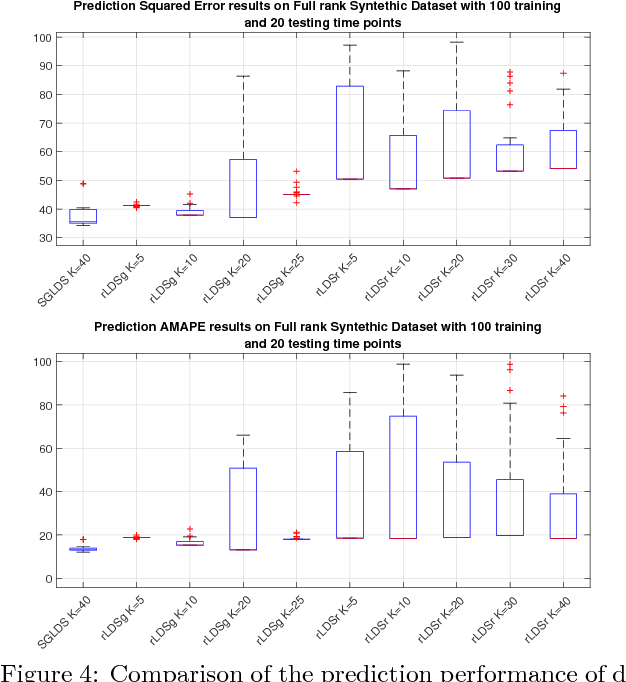
A nonparametric Bayesian sparse graph linear dynamical system (SGLDS) is proposed to model sequentially observed multivariate data. SGLDS uses the Bernoulli-Poisson link together with a gamma process to generate an infinite dimensional sparse random graph to model state transitions. Depending on the sparsity pattern of the corresponding row and column of the graph affinity matrix, a latent state of SGLDS can be categorized as either a non-dynamic state or a dynamic one. A normal-gamma construction is used to shrink the energy captured by the non-dynamic states, while the dynamic states can be further categorized into live, absorbing, or noise-injection states, which capture different types of dynamical components of the underlying time series. The state-of-the-art performance of SGLDS is demonstrated with experiments on both synthetic and real data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge