Non-Intrusive Speech Intelligibility Prediction for Hearing-Impaired Users using Intermediate ASR Features and Human Memory Models
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2024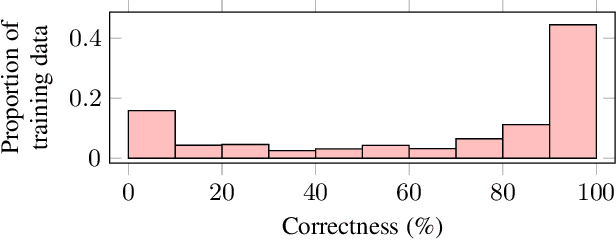
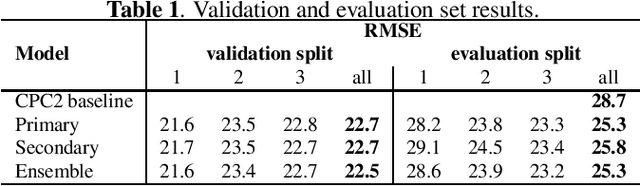
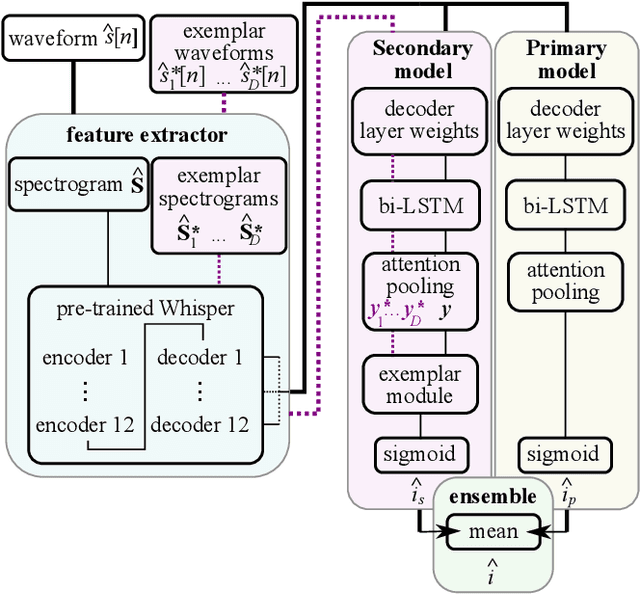
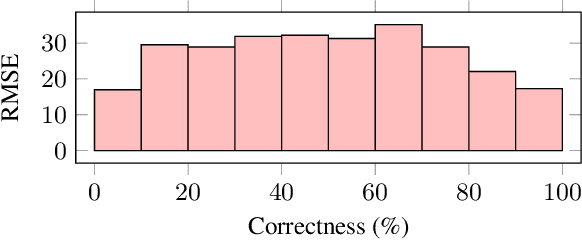
Neural networks have been successfully used for non-intrusive speech intelligibility prediction. Recently, the use of feature representations sourced from intermediate layers of pre-trained self-supervised and weakly-supervised models has been found to be particularly useful for this task. This work combines the use of Whisper ASR decoder layer representations as neural network input features with an exemplar-based, psychologically motivated model of human memory to predict human intelligibility ratings for hearing-aid users. Substantial performance improvement over an established intrusive HASPI baseline system is found, including on enhancement systems and listeners unseen in the training data, with a root mean squared error of 25.3 compared with the baseline of 28.7.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge