Noisier2Noise: Learning to Denoise from Unpaired Noisy Data
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2019
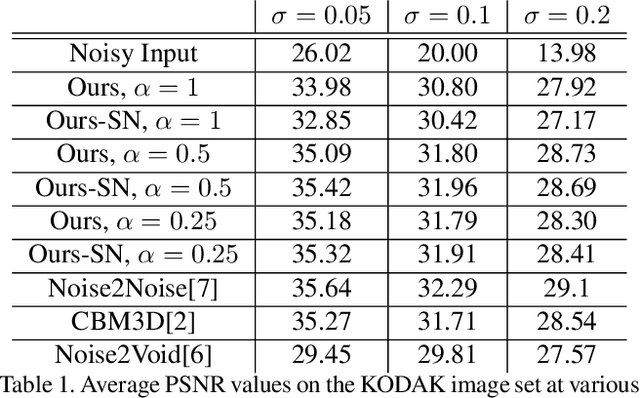
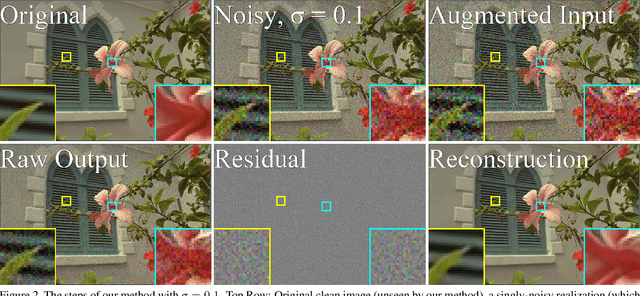
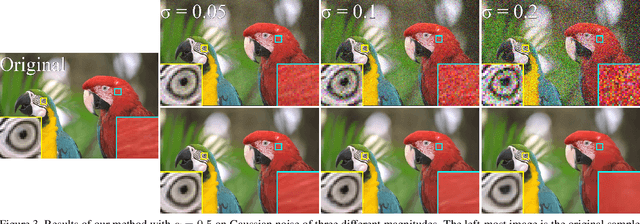
We present a method for training a neural network to perform image denoising without access to clean training examples or access to paired noisy training examples. Our method requires only a single noisy realization of each training example and a statistical model of the noise distribution, and is applicable to a wide variety of noise models, including spatially structured noise. Our model produces results which are competitive with other learned methods which require richer training data, and outperforms traditional non-learned denoising methods. We present derivations of our method for arbitrary additive noise, an improvement specific to Gaussian additive noise, and an extension to multiplicative Bernoulli noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge