Node metadata can produce predictability transitions in network inference problems
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2021
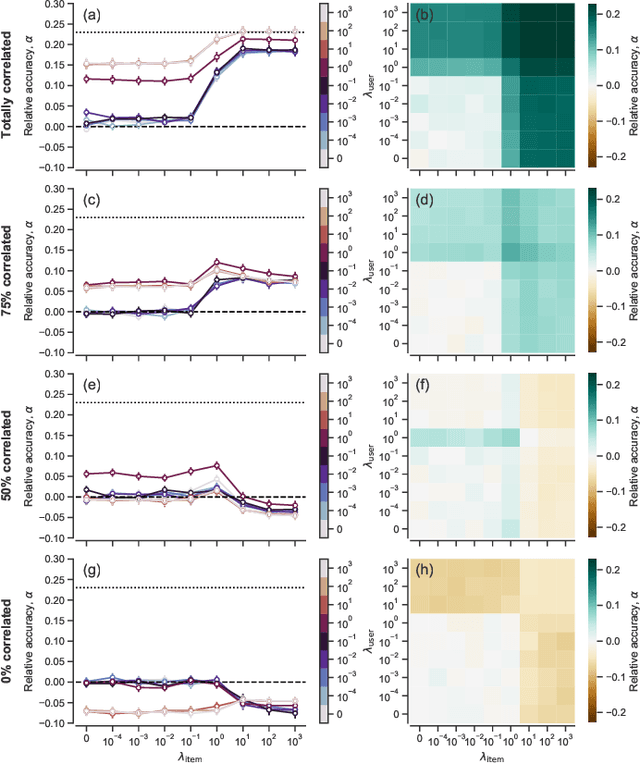
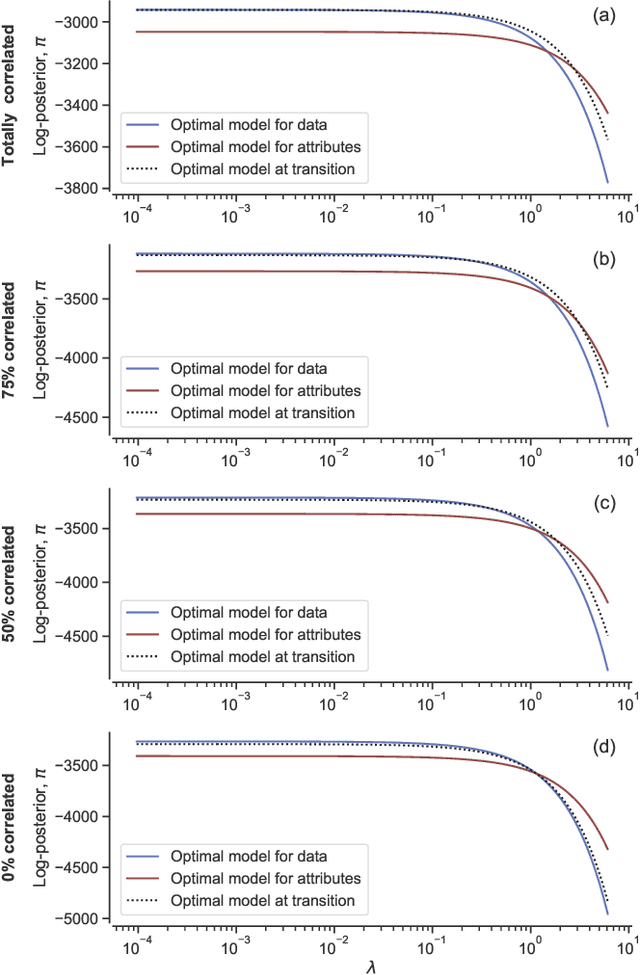
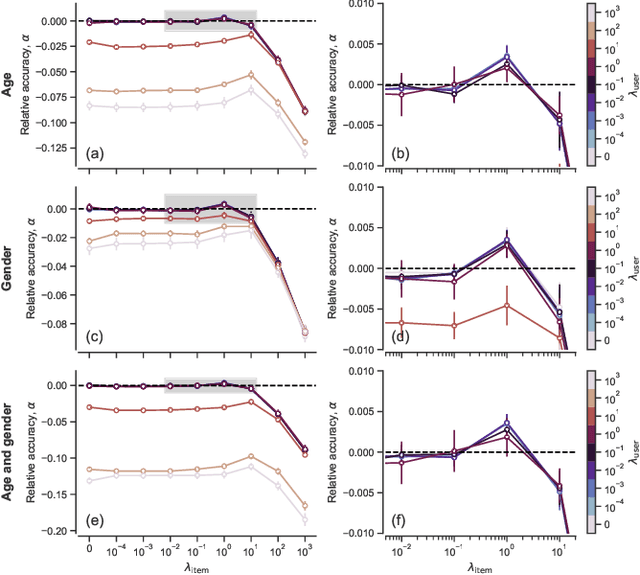
Network inference is the process of learning the properties of complex networks from data. Besides using information about known links in the network, node attributes and other forms of network metadata can help to solve network inference problems. Indeed, several approaches have been proposed to introduce metadata into probabilistic network models and to use them to make better inferences. However, we know little about the effect of such metadata in the inference process. Here, we investigate this issue. We find that, rather than affecting inference gradually, adding metadata causes abrupt transitions in the inference process and in our ability to make accurate predictions, from a situation in which metadata does not play any role to a situation in which metadata completely dominates the inference process. When network data and metadata are partly correlated, metadata optimally contributes to the inference process at the transition between data-dominated and metadata-dominated regimes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge