Neuron Patching: Neuron-level Model Editing on Code Generation and LLMs
Paper and Code
Dec 08, 2023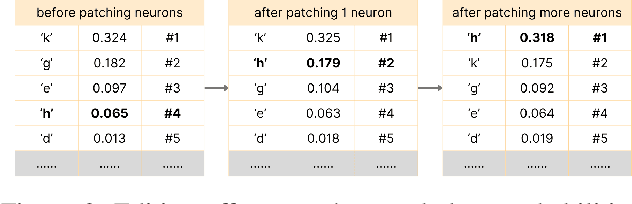
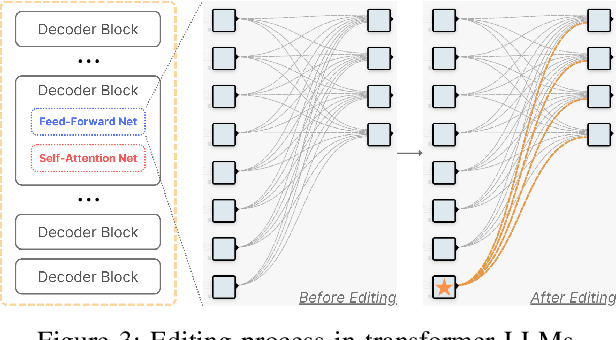
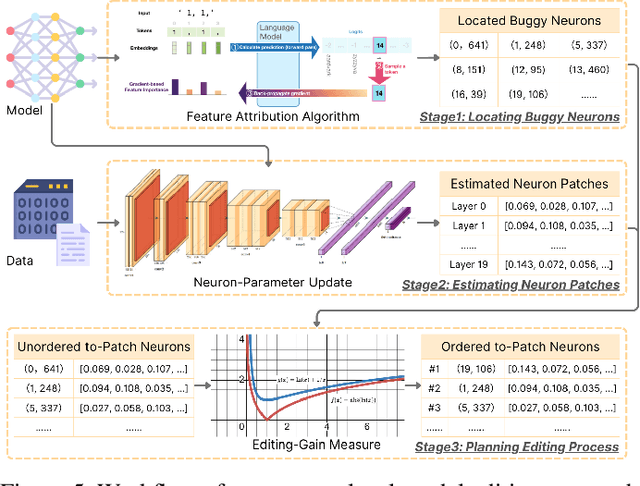
Large Language Models are successfully adopted in software engineering, especially in code generation. Updating these models with new knowledge is very expensive, and is often required to fully realize their value. In this paper, we propose a novel and effective model editing approach, \textsc{MENT}, to patch LLMs in coding tasks. Based on the mechanism of generative LLMs, \textsc{MENT} enables model editing in next-token predictions, and further supports common coding tasks. \textsc{MENT} is effective, efficient, and reliable. It can correct a neural model by patching 1 or 2 neurons. As the pioneer work on neuron-level model editing of generative models, we formalize the editing process and introduce the involved concepts. Besides, we also introduce new measures to evaluate its generalization ability, and build a benchmark for further study. Our approach is evaluated on three coding tasks, including API-seq recommendation, line-level code generation, and pseudocode-to-code transaction. It outperforms the state-of-the-art by a significant margin on both effectiveness and efficiency measures. In addition, we demonstrate the usages of \textsc{MENT} for LLM reasoning in software engineering. By editing the LLM knowledge with \textsc{MENT}, the directly or indirectly dependent behaviors in the chain-of-thought change accordingly and automatically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge