Neurally Augmented ALISTA
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2020
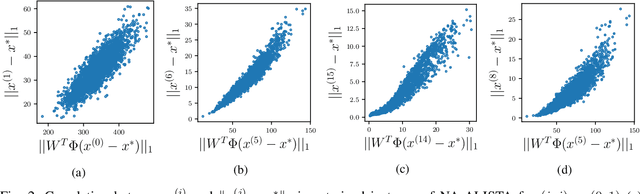
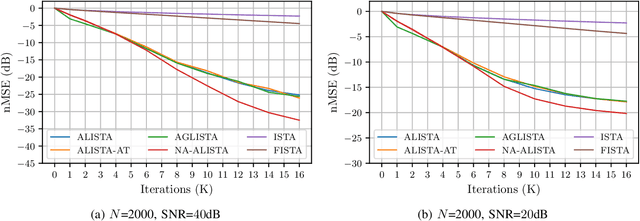
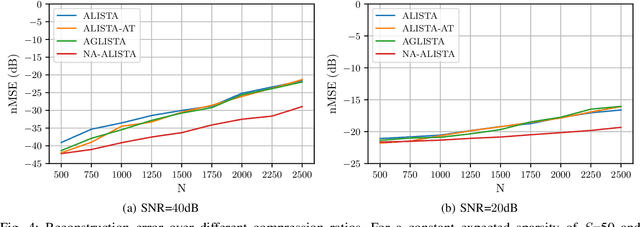
It is well-established that many iterative sparse reconstruction algorithms can be unrolled to yield a learnable neural network for improved empirical performance. A prime example is learned ISTA (LISTA) where weights, step sizes and thresholds are learned from training data. Recently, Analytic LISTA (ALISTA) has been introduced, combining the strong empirical performance of a fully learned approach like LISTA, while retaining theoretical guarantees of classical compressed sensing algorithms and significantly reducing the number of parameters to learn. However, these parameters are trained to work in expectation, often leading to suboptimal reconstruction of individual targets. In this work we therefore introduce Neurally Augmented ALISTA, in which an LSTM network is used to compute step sizes and thresholds individually for each target vector during reconstruction. This adaptive approach is theoretically motivated by revisiting the recovery guarantees of ALISTA. We show that our approach further improves empirical performance in sparse reconstruction, in particular outperforming existing algorithms by an increasing margin as the compression ratio becomes more challenging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge