Neural machine translation for automated feedback on children's early-stage writing
Paper and Code
Nov 15, 2023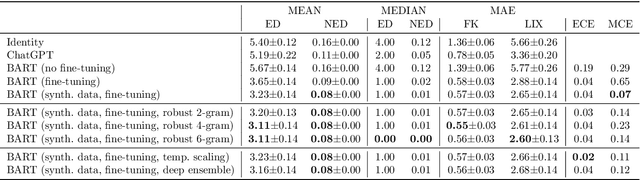
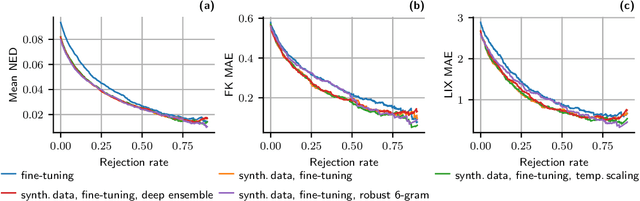
In this work, we address the problem of assessing and constructing feedback for early-stage writing automatically using machine learning. Early-stage writing is typically vastly different from conventional writing due to phonetic spelling and lack of proper grammar, punctuation, spacing etc. Consequently, early-stage writing is highly non-trivial to analyze using common linguistic metrics. We propose to use sequence-to-sequence models for "translating" early-stage writing by students into "conventional" writing, which allows the translated text to be analyzed using linguistic metrics. Furthermore, we propose a novel robust likelihood to mitigate the effect of noise in the dataset. We investigate the proposed methods using a set of numerical experiments and demonstrate that the conventional text can be predicted with high accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge