Narrowing the Gap: Improved Detector Training with Noisy Location Annotations
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2022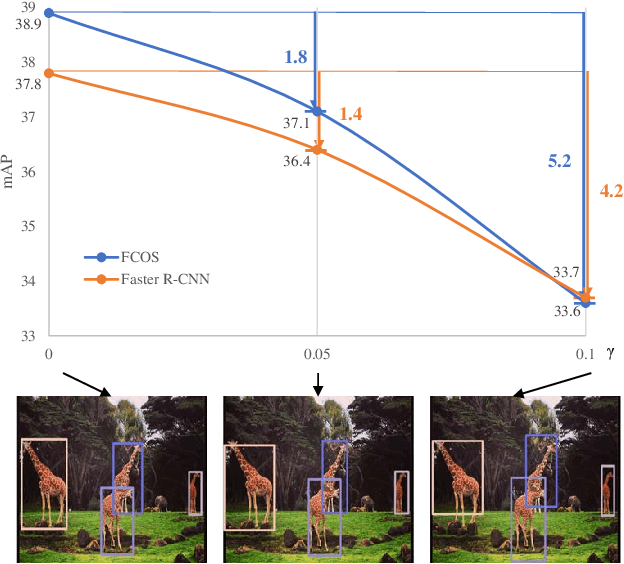
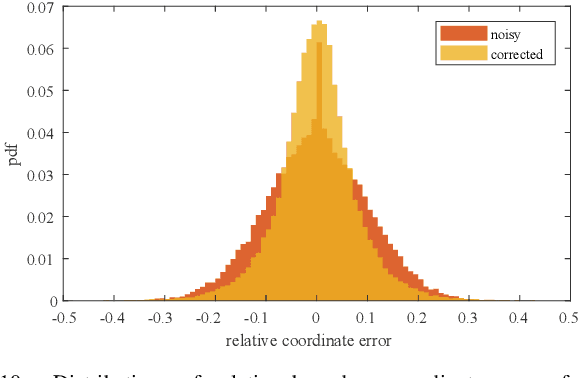

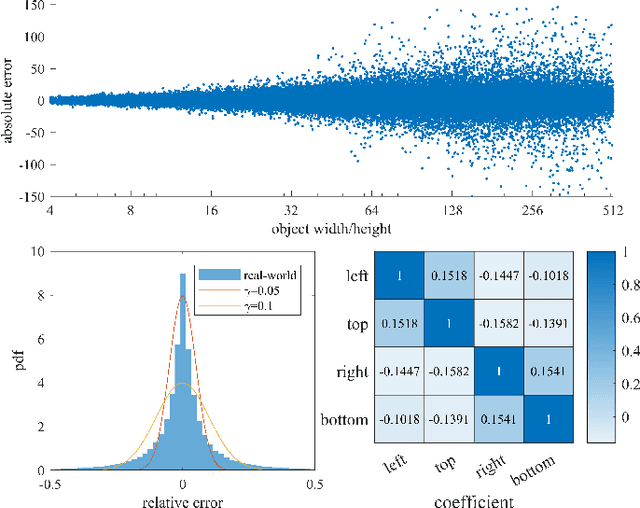
Deep learning methods require massive of annotated data for optimizing parameters. For example, datasets attached with accurate bounding box annotations are essential for modern object detection tasks. However, labeling with such pixel-wise accuracy is laborious and time-consuming, and elaborate labeling procedures are indispensable for reducing man-made noise, involving annotation review and acceptance testing. In this paper, we focus on the impact of noisy location annotations on the performance of object detection approaches and aim to, on the user side, reduce the adverse effect of the noise. First, noticeable performance degradation is experimentally observed for both one-stage and two-stage detectors when noise is introduced to the bounding box annotations. For instance, our synthesized noise results in performance decrease from 38.9% AP to 33.6% AP for FCOS detector on COCO test split, and 37.8%AP to 33.7%AP for Faster R-CNN. Second, a self-correction technique based on a Bayesian filter for prediction ensemble is proposed to better exploit the noisy location annotations following a Teacher-Student learning paradigm. Experiments for both synthesized and real-world scenarios consistently demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, e.g., our method increases the degraded performance of the FCOS detector from 33.6% AP to 35.6% AP on COCO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge