Multiscale Matching Driven by Cross-Modal Similarity Consistency for Audio-Text Retrieval
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2024


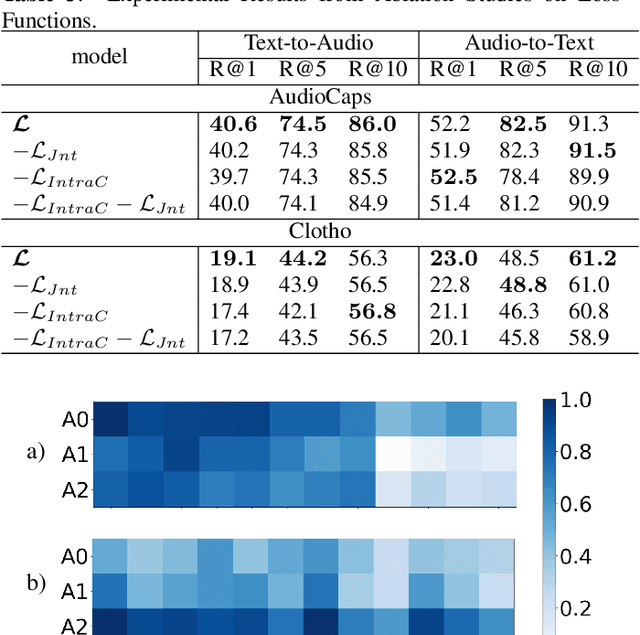
Audio-text retrieval (ATR), which retrieves a relevant caption given an audio clip (A2T) and vice versa (T2A), has recently attracted much research attention. Existing methods typically aggregate information from each modality into a single vector for matching, but this sacrifices local details and can hardly capture intricate relationships within and between modalities. Furthermore, current ATR datasets lack comprehensive alignment information, and simple binary contrastive learning labels overlook the measurement of fine-grained semantic differences between samples. To counter these challenges, we present a novel ATR framework that comprehensively captures the matching relationships of multimodal information from different perspectives and finer granularities. Specifically, a fine-grained alignment method is introduced, achieving a more detail-oriented matching through a multiscale process from local to global levels to capture meticulous cross-modal relationships. In addition, we pioneer the application of cross-modal similarity consistency, leveraging intra-modal similarity relationships as soft supervision to boost more intricate alignment. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach, outperforming previous methods by significant margins of at least 3.9% (T2A) / 6.9% (A2T) R@1 on the AudioCaps dataset and 2.9% (T2A) / 5.4% (A2T) R@1 on the Clotho dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge