Multilinear Tensor Low-Rank Approximation for Policy-Gradient Methods in Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2025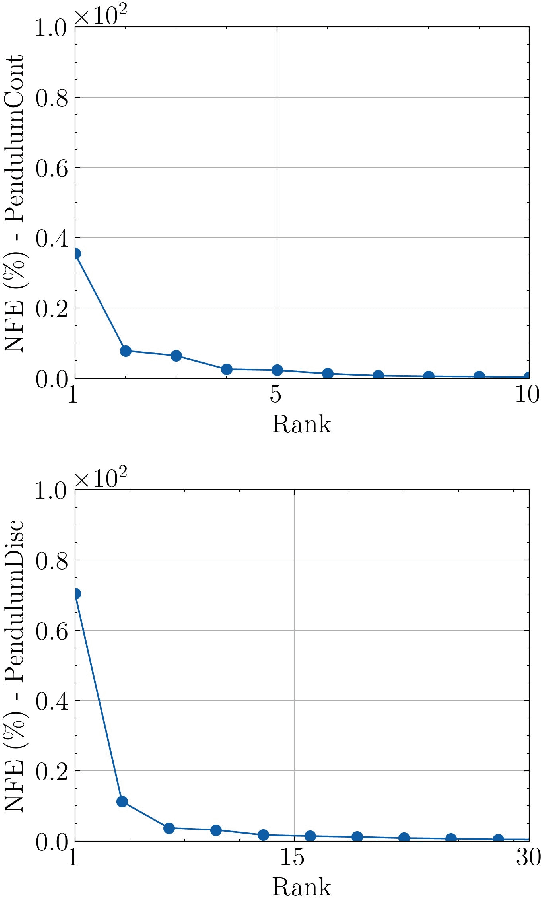
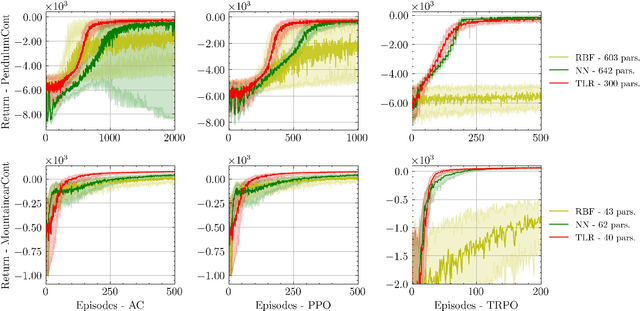
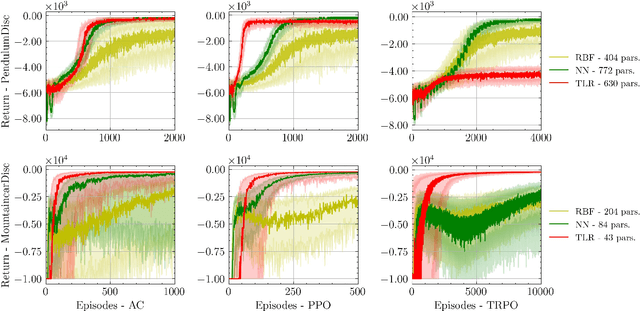
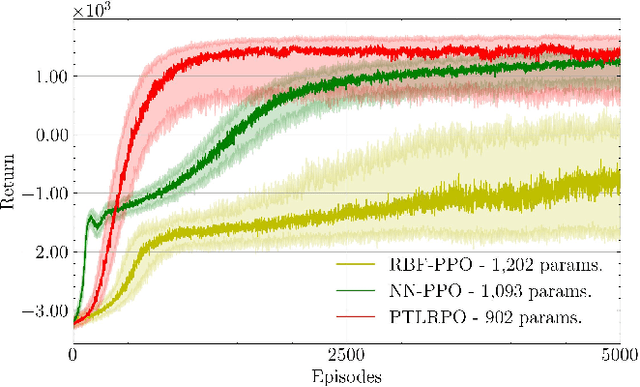
Reinforcement learning (RL) aims to estimate the action to take given a (time-varying) state, with the goal of maximizing a cumulative reward function. Predominantly, there are two families of algorithms to solve RL problems: value-based and policy-based methods, with the latter designed to learn a probabilistic parametric policy from states to actions. Most contemporary approaches implement this policy using a neural network (NN). However, NNs usually face issues related to convergence, architectural suitability, hyper-parameter selection, and underutilization of the redundancies of the state-action representations (e.g. locally similar states). This paper postulates multi-linear mappings to efficiently estimate the parameters of the RL policy. More precisely, we leverage the PARAFAC decomposition to design tensor low-rank policies. The key idea involves collecting the policy parameters into a tensor and leveraging tensor-completion techniques to enforce low rank. We establish theoretical guarantees of the proposed methods for various policy classes and validate their efficacy through numerical experiments. Specifically, we demonstrate that tensor low-rank policy models reduce computational and sample complexities in comparison to NN models while achieving similar rewards.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge