Multi-view Tracking Using Weakly Supervised Human Motion Prediction
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2022
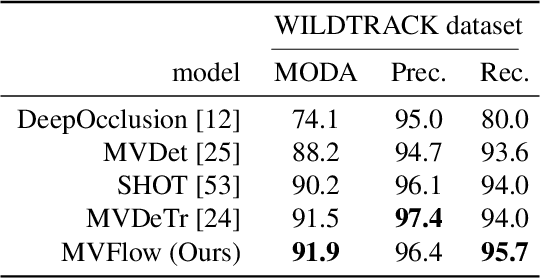
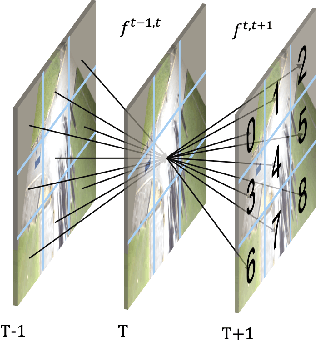

Multi-view approaches to people-tracking have the potential to better handle occlusions than single-view ones in crowded scenes. They often rely on the tracking-by-detection paradigm, which involves detecting people first and then connecting the detections. In this paper, we argue that an even more effective approach is to predict people motion over time and infer people's presence in individual frames from these. This enables to enforce consistency both over time and across views of a single temporal frame. We validate our approach on the PETS2009 and WILDTRACK datasets and demonstrate that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
* Accepted at WACV 2023
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge