Multi-Task, Multi-Domain Deep Segmentation with Shared Representations and Contrastive Regularization for Sparse Pediatric Datasets
Paper and Code
May 21, 2021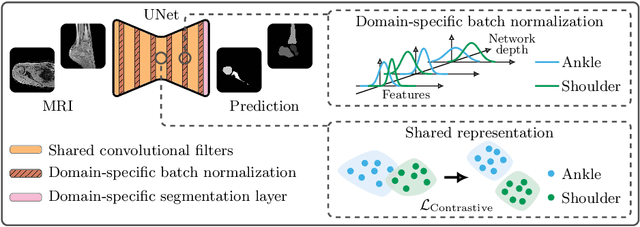



Automatic segmentation of magnetic resonance (MR) images is crucial for morphological evaluation of the pediatric musculoskeletal system in clinical practice. However, the accuracy and generalization performance of individual segmentation models are limited due to the restricted amount of annotated pediatric data. Hence, we propose to train a segmentation model on multiple datasets, arising from different parts of the anatomy, in a multi-task and multi-domain learning framework. This approach allows to overcome the inherent scarcity of pediatric data while benefiting from a more robust shared representation. The proposed segmentation network comprises shared convolutional filters, domain-specific batch normalization parameters that compute the respective dataset statistics and a domain-specific segmentation layer. Furthermore, a supervised contrastive regularization is integrated to further improve generalization capabilities, by promoting intra-domain similarity and impose inter-domain margins in embedded space. We evaluate our contributions on two pediatric imaging datasets of the ankle and shoulder joints for bone segmentation. Results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge