Multi Task Deep Morphological Analyzer: Context Aware Joint Morphological Tagging and Lemma Prediction
Paper and Code
Nov 21, 2018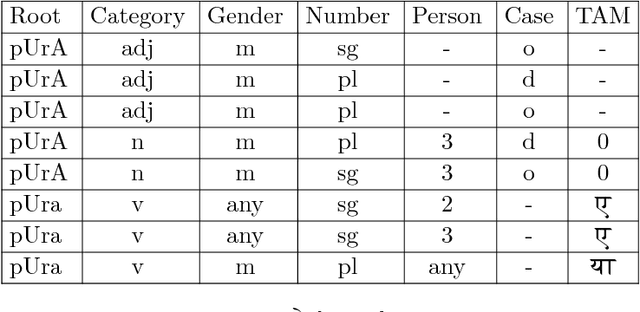
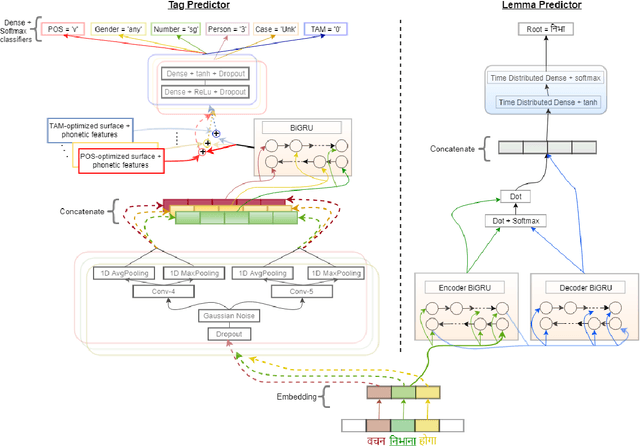
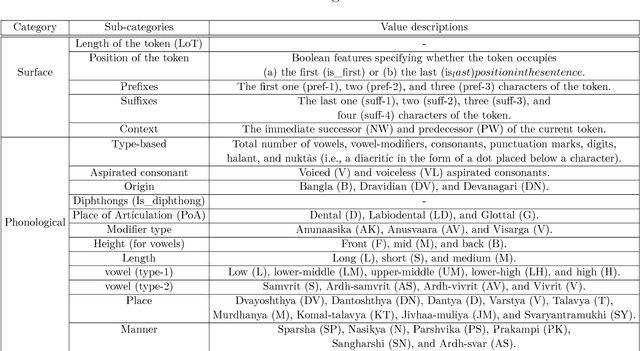
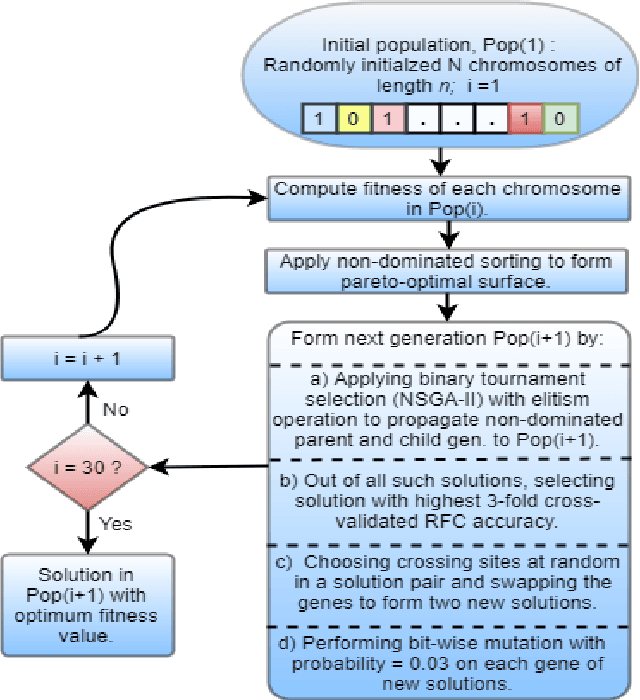
Morphological analysis is an important first step in downstream tasks like machine translation and dependency parsing of morphologically rich languages (MRLs) such as those belonging to Indo-Aryan and Dravidian families. However, the ambiguities introduced by the recombination of morphemes constructing several possible inflections for a word makes the prediction of syntactic traits a notoriously complicated task for MRLs. We propose a character-level neural morphological analyzer, the Multi Task Deep Morphological analyzer (MT-DMA), based on multitask learning of word-level tag markers for Hindi. In order to show the portability of our system to other related languages, we present results on Urdu too. MT-DMA predicts the complete set of morphological tags for words of Indo-Aryan languages: Parts-of-speech (POS), Gender (G), Number (N), Person (P), Case (C), Tense-Aspect-Modality (TAM) marker as well as the Lemma (L) by jointly learning all these in a single end-to-end framework. We show the effectiveness of training of such deep neural networks by the simultaneous optimization of multiple loss functions and sharing of initial parameters for context-aware morphological analysis. Our model outperforms the state-of-art analyzers for Hindi and Urdu. Exploring the use of a set of character-level features in phonological space optimized for each tag through a multi-objective genetic algorithm, coupled with effective training strategies, our model establishes a new state-of-the-art accuracy score upon all seven of the tasks for both the languages. MT-DMA is publicly accessible to be used at http://35.154.251.44/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge