Multi-relation Message Passing for Multi-label Text Classification
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2022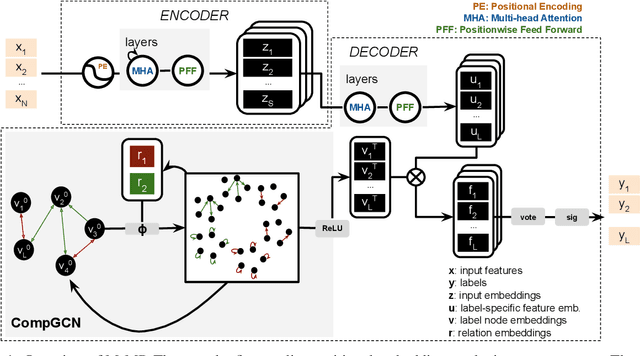
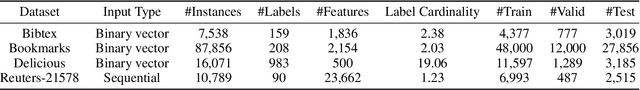
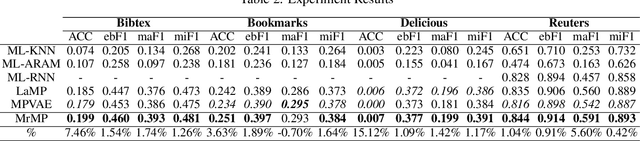
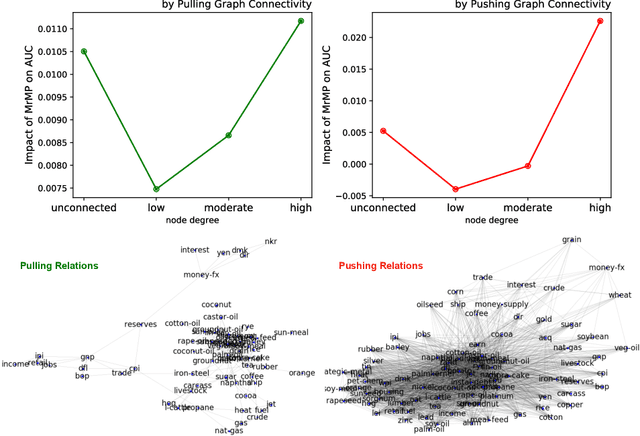
A well-known challenge associated with the multi-label classification problem is modelling dependencies between labels. Most attempts at modelling label dependencies focus on co-occurrences, ignoring the valuable information that can be extracted by detecting label subsets that rarely occur together. For example, consider customer product reviews; a product probably would not simultaneously be tagged by both "recommended" (i.e., reviewer is happy and recommends the product) and "urgent" (i.e., the review suggests immediate action to remedy an unsatisfactory experience). Aside from the consideration of positive and negative dependencies, the direction of a relationship should also be considered. For a multi-label image classification problem, the "ship" and "sea" labels have an obvious dependency, but the presence of the former implies the latter much more strongly than the other way around. These examples motivate the modelling of multiple types of bi-directional relationships between labels. In this paper, we propose a novel method, entitled Multi-relation Message Passing (MrMP), for the multi-label classification problem. Experiments on benchmark multi-label text classification datasets show that the MrMP module yields similar or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. The approach imposes only minor additional computational and memory overheads.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge