Multi-Objective Algorithms for Learning Open-Ended Robotic Problems
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2024
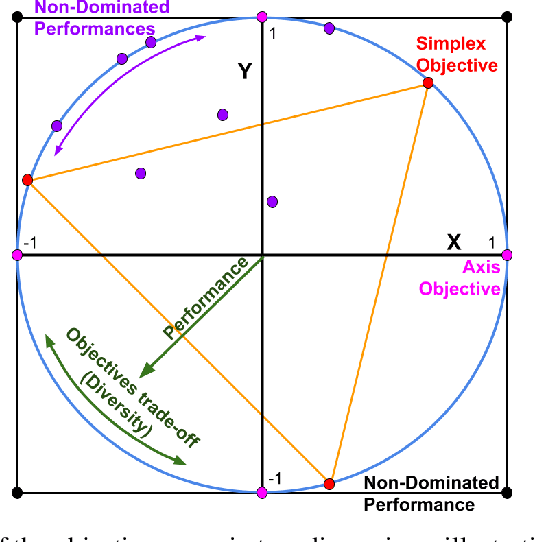
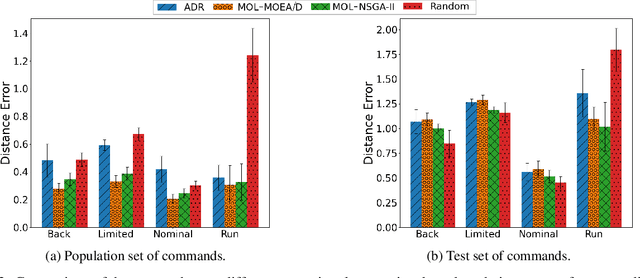
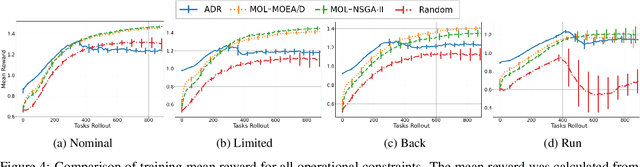
Quadrupedal locomotion is a complex, open-ended problem vital to expanding autonomous vehicle reach. Traditional reinforcement learning approaches often fall short due to training instability and sample inefficiency. We propose a novel method leveraging multi-objective evolutionary algorithms as an automatic curriculum learning mechanism, which we named Multi-Objective Learning (MOL). Our approach significantly enhances the learning process by projecting velocity commands into an objective space and optimizing for both performance and diversity. Tested within the MuJoCo physics simulator, our method demonstrates superior stability and adaptability compared to baseline approaches. As such, it achieved 19\% and 44\% fewer errors against our best baseline algorithm in difficult scenarios based on a uniform and tailored evaluation respectively. This work introduces a robust framework for training quadrupedal robots, promising significant advancements in robotic locomotion and open-ended robotic problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge