Multi-layer Clustering-based Residual Sparsifying Transform for Low-dose CT Image Reconstruction
Paper and Code
Mar 22, 2022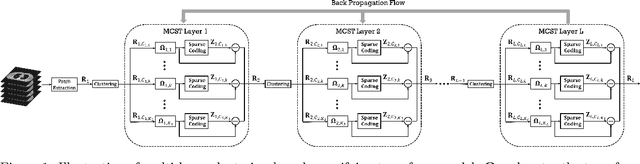

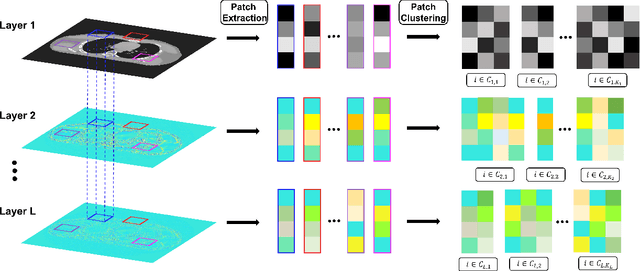
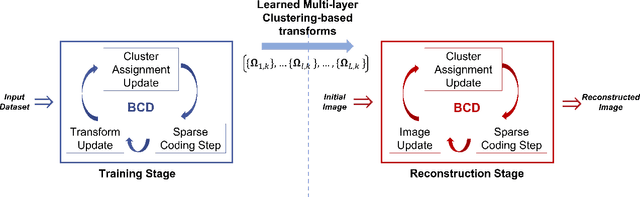
The recently proposed sparsifying transform models incur low computational cost and have been applied to medical imaging. Meanwhile, deep models with nested network structure reveal great potential for learning features in different layers. In this study, we propose a network-structured sparsifying transform learning approach for X-ray computed tomography (CT), which we refer to as multi-layer clustering-based residual sparsifying transform (MCST) learning. The proposed MCST scheme learns multiple different unitary transforms in each layer by dividing each layer's input into several classes. We apply the MCST model to low-dose CT (LDCT) reconstruction by deploying the learned MCST model into the regularizer in penalized weighted least squares (PWLS) reconstruction. We conducted LDCT reconstruction experiments on XCAT phantom data and Mayo Clinic data and trained the MCST model with 2 (or 3) layers and with 5 clusters in each layer. The learned transforms in the same layer showed rich features while additional information is extracted from representation residuals. Our simulation results demonstrate that PWLS-MCST achieves better image reconstruction quality than the conventional FBP method and PWLS with edge-preserving (EP) regularizer. It also outperformed recent advanced methods like PWLS with a learned multi-layer residual sparsifying transform prior (MARS) and PWLS with a union of learned transforms (ULTRA), especially for displaying clear edges and preserving subtle details.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge