Multi-Domain Evolutionary Optimization of Network Structures
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2024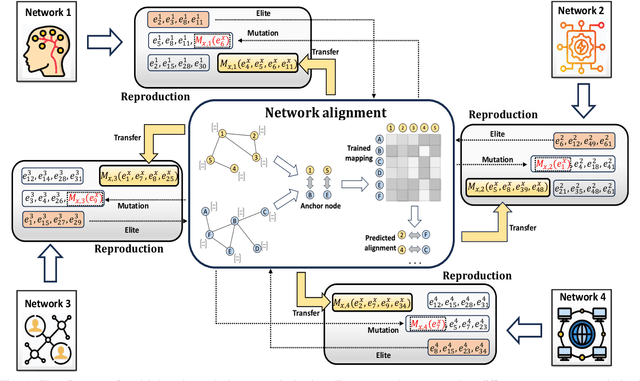
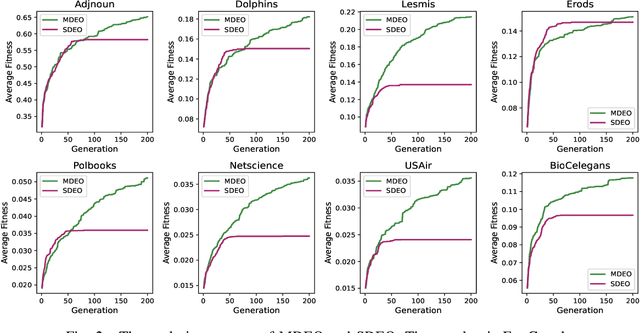
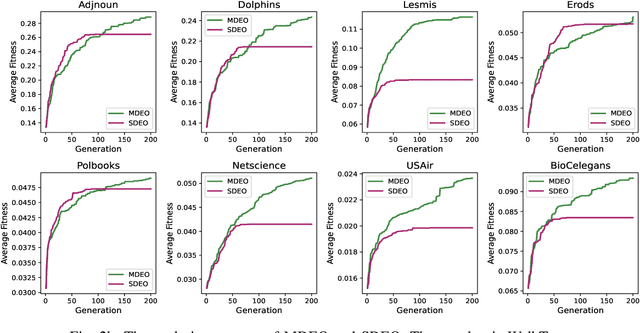
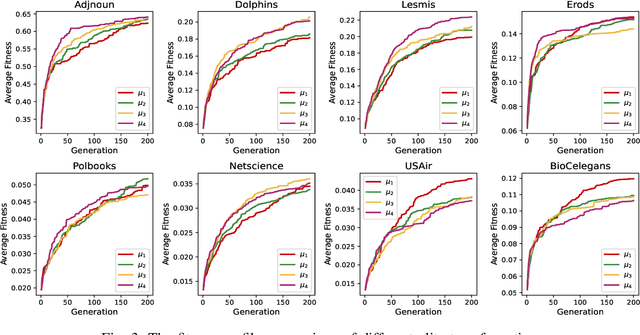
Multi-Task Evolutionary Optimization (MTEO), an important field focusing on addressing complex problems through optimizing multiple tasks simultaneously, has attracted much attention. While MTEO has been primarily focusing on task similarity, there remains a hugely untapped potential in harnessing the shared characteristics between different domains to enhance evolutionary optimization. For example, real-world complex systems usually share the same characteristics, such as the power-law rule, small-world property, and community structure, thus making it possible to transfer solutions optimized in one system to another to facilitate the optimization. Drawing inspiration from this observation of shared characteristics within complex systems, we set out to extend MTEO to a novel framework - multi-domain evolutionary optimization (MDEO). To examine the performance of the proposed MDEO, we utilize a challenging combinatorial problem of great security concern - community deception in complex networks as the optimization task. To achieve MDEO, we propose a community-based measurement of graph similarity to manage the knowledge transfer among domains. Furthermore, we develop a graph representation-based network alignment model that serves as the conduit for effectively transferring solutions between different domains. Moreover, we devise a self-adaptive mechanism to determine the number of transferred solutions from different domains and introduce a novel mutation operator based on the learned mapping to facilitate the utilization of knowledge from other domains. Experiments on eight real-world networks of different domains demonstrate MDEO superiority in efficacy compared to classical evolutionary optimization. Simulations of attacks on the community validate the effectiveness of the proposed MDEO in safeguarding community security.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge