Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning for Resource Allocation in IoT networks with Edge Computing
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2020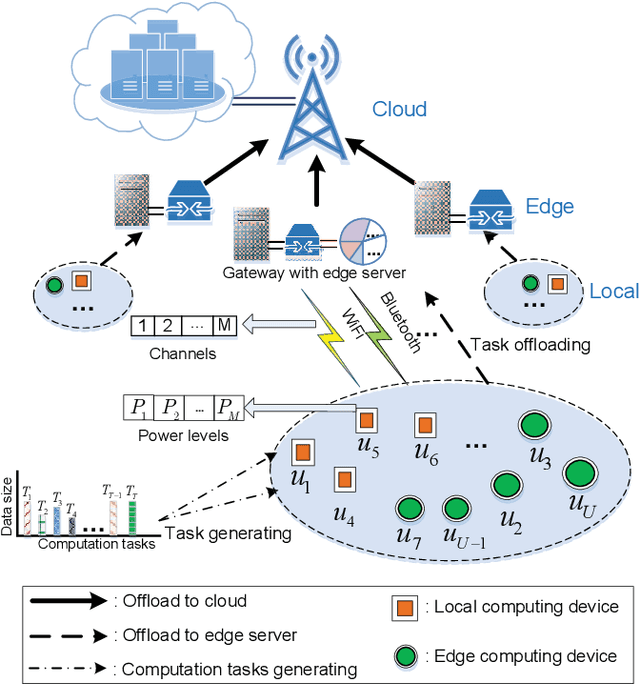
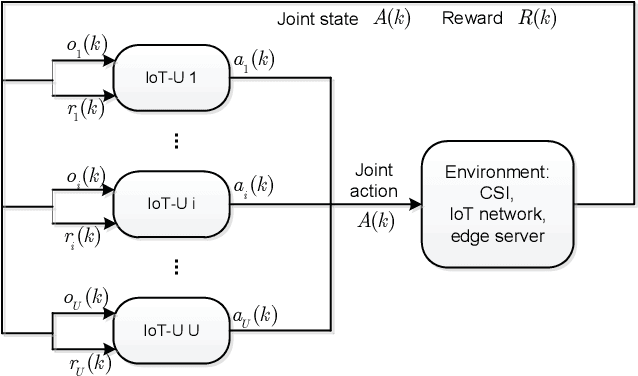
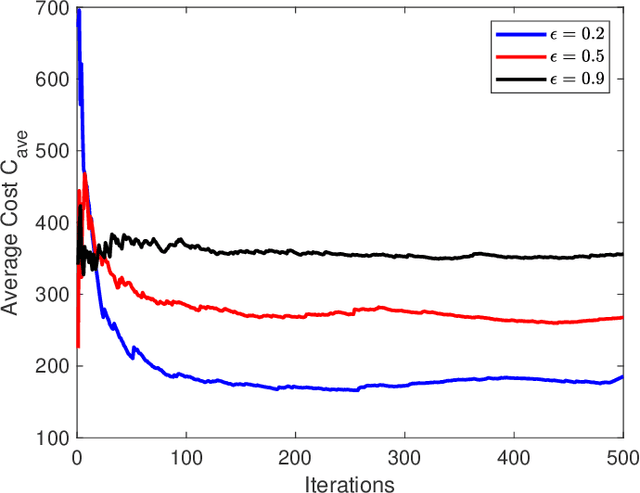
To support popular Internet of Things (IoT) applications such as virtual reality, mobile games and wearable devices, edge computing provides a front-end distributed computing archetype of centralized cloud computing with low latency. However, it's challenging for end users to offload computation due to their massive requirements on spectrum and computation resources and frequent requests on Radio Access Technology (RAT). In this paper, we investigate computation offloading mechanism with resource allocation in IoT edge computing networks by formulating it as a stochastic game. Here, each end user is a learning agent observing its local environment to learn optimal decisions on either local computing or edge computing with the goal of minimizing long term system cost by choosing its transmit power level, RAT and sub-channel without knowing any information of the other end users. Therefore, a multi-agent reinforcement learning framework is developed to solve the stochastic game with a proposed independent learners based multi-agent Q-learning (IL-based MA-Q) algorithm. Simulations demonstrate that the proposed IL-based MA-Q algorithm is feasible to solve the formulated problem and is more energy efficient without extra cost on channel estimation at the centralized gateway compared to the other two benchmark algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge