Multi-agent Databases via Independent Learning
Paper and Code
May 28, 2022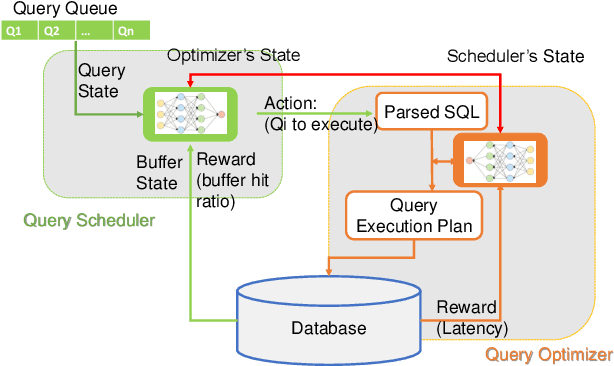
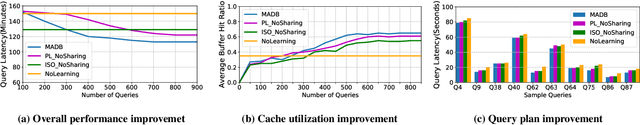
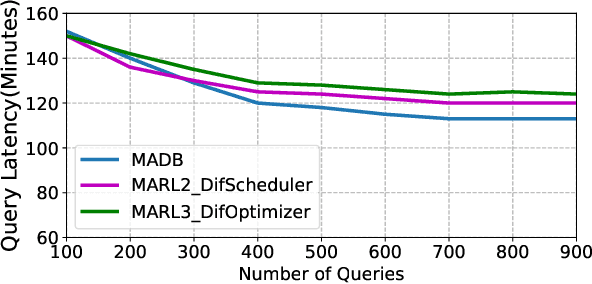
Machine learning is rapidly being used in database research to improve the effectiveness of numerous tasks included but not limited to query optimization, workload scheduling, physical design, etc. essential database components, such as the optimizer, scheduler, and physical designer. Currently, the research focus has been on replacing a single database component responsible for one task by its learning-based counterpart. However, query performance is not simply determined by the performance of a single component, but by the cooperation of multiple ones. As such, learned based database components need to collaborate during both training and execution in order to develop policies that meet end performance goals. Thus, the paper attempts to address the question "Is it possible to design a database consisting of various learned components that cooperatively work to improve end-to-end query latency?". To answer this question, we introduce MADB (Multi-Agent DB), a proof-of-concept system that incorporates a learned query scheduler and a learned query optimizer. MADB leverages a cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning approach that allows the two components to exchange the context of their decisions with each other and collaboratively work towards reducing the query latency. Preliminary results demonstrate that MADB can outperform the non-cooperative integration of learned components.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge