Multi-Agent Cross-Translated Diversification for Unsupervised Machine Translation
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2020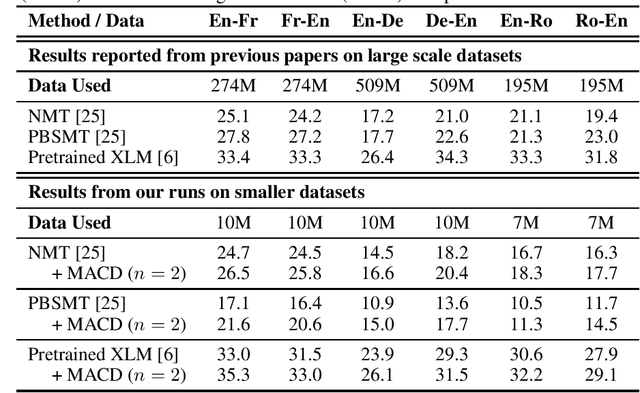

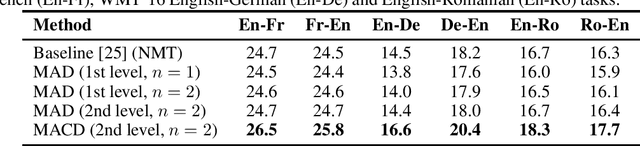
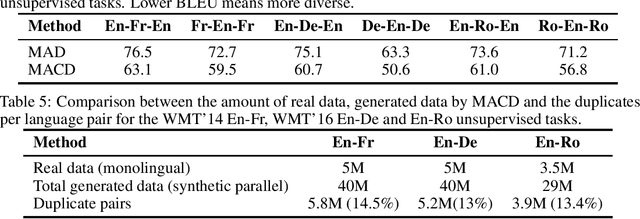
Recent unsupervised machine translation (UMT) systems usually employ three main principles: initialization, language modeling and iterative back-translation, though they may apply these principles differently. This work introduces another component to this framework: Multi-Agent Cross-translated Diversification (MACD). The method trains multiple UMT agents and then translates monolingual data back and forth using non-duplicative agents to acquire synthetic parallel data for supervised MT. MACD is applicable to all previous UMT approaches. In our experiments, the technique boosts the performance for some commonly used UMT methods by 1.5-2.0 BLEU. In particular, in WMT'14 English-French, WMT'16 German-English and English-Romanian, MACD outperforms cross-lingual masked language model pretraining by 2.3, 2.2 and 1.6 BLEU, respectively. It also yields 1.5-3.3 BLEU improvements in IWSLT English-French and English-German translation tasks. Through extensive experimental analyses, we show that MACD is effective because it embraces data diversity while other similar variants do not.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge