MT-BioNER: Multi-task Learning for Biomedical Named Entity Recognition using Deep Bidirectional Transformers
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2020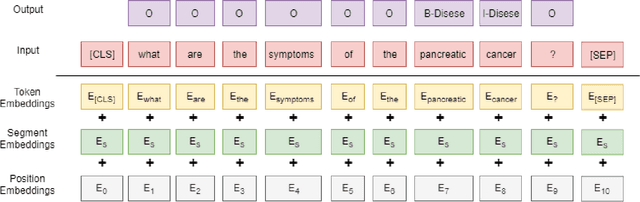


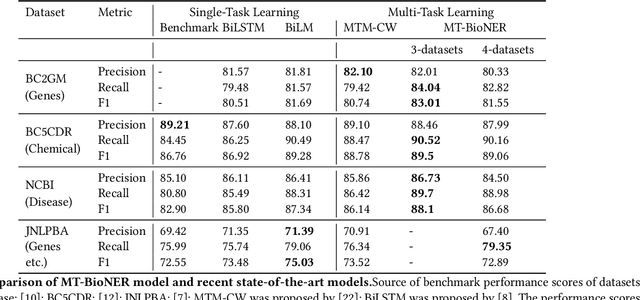
Conversational agents such as Cortana, Alexa and Siri are continuously working on increasing their capabilities by adding new domains. The support of a new domain includes the design and development of a number of NLU components for domain classification, intents classification and slots tagging (including named entity recognition). Each component only performs well when trained on a large amount of labeled data. Second, these components are deployed on limited-memory devices which requires some model compression. Third, for some domains such as the health domain, it is hard to find a single training data set that covers all the required slot types. To overcome these mentioned problems, we present a multi-task transformer-based neural architecture for slot tagging. We consider the training of a slot tagger using multiple data sets covering different slot types as a multi-task learning problem. The experimental results on the biomedical domain have shown that the proposed approach outperforms the previous state-of-the-art systems for slot tagging on the different benchmark biomedical datasets in terms of (time and memory) efficiency and effectiveness. The output slot tagger can be used by the conversational agent to better identify entities in the input utterances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge