Motion Question Answering via Modular Motion Programs
Paper and Code
May 17, 2023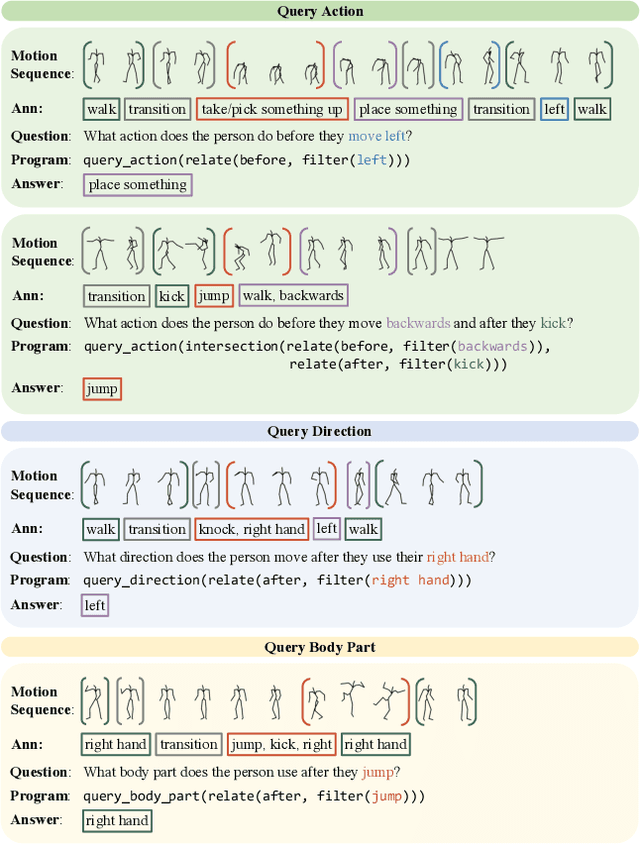
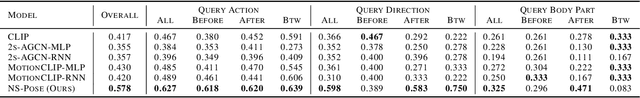
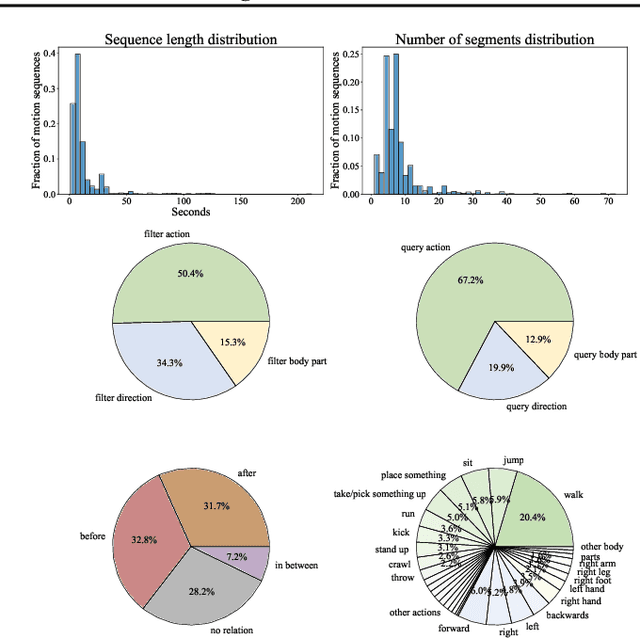
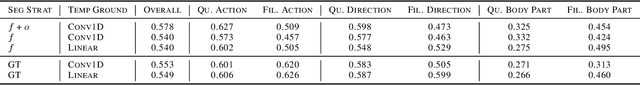
In order to build artificial intelligence systems that can perceive and reason with human behavior in the real world, we must first design models that conduct complex spatio-temporal reasoning over motion sequences. Moving towards this goal, we propose the HumanMotionQA task to evaluate complex, multi-step reasoning abilities of models on long-form human motion sequences. We generate a dataset of question-answer pairs that require detecting motor cues in small portions of motion sequences, reasoning temporally about when events occur, and querying specific motion attributes. In addition, we propose NSPose, a neuro-symbolic method for this task that uses symbolic reasoning and a modular design to ground motion through learning motion concepts, attribute neural operators, and temporal relations. We demonstrate the suitability of NSPose for the HumanMotionQA task, outperforming all baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge