Model-Based Decentralized Policy Optimization
Paper and Code
Feb 16, 2023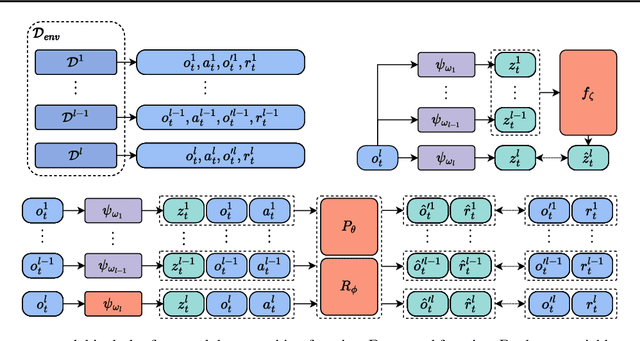

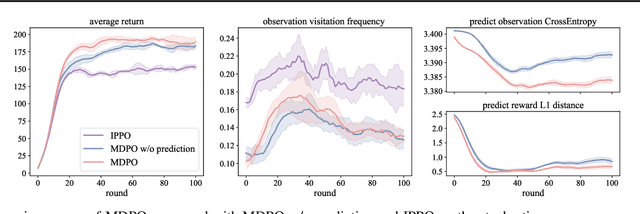
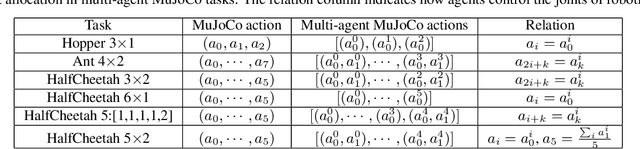
Decentralized policy optimization has been commonly used in cooperative multi-agent tasks. However, since all agents are updating their policies simultaneously, from the perspective of individual agents, the environment is non-stationary, resulting in it being hard to guarantee monotonic policy improvement. To help the policy improvement be stable and monotonic, we propose model-based decentralized policy optimization (MDPO), which incorporates a latent variable function to help construct the transition and reward function from an individual perspective. We theoretically analyze that the policy optimization of MDPO is more stable than model-free decentralized policy optimization. Moreover, due to non-stationarity, the latent variable function is varying and hard to be modeled. We further propose a latent variable prediction method to reduce the error of the latent variable function, which theoretically contributes to the monotonic policy improvement. Empirically, MDPO can indeed obtain superior performance than model-free decentralized policy optimization in a variety of cooperative multi-agent tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge