MKANet: A Lightweight Network with Sobel Boundary Loss for Efficient Land-cover Classification of Satellite Remote Sensing Imagery
Paper and Code
Jul 28, 2022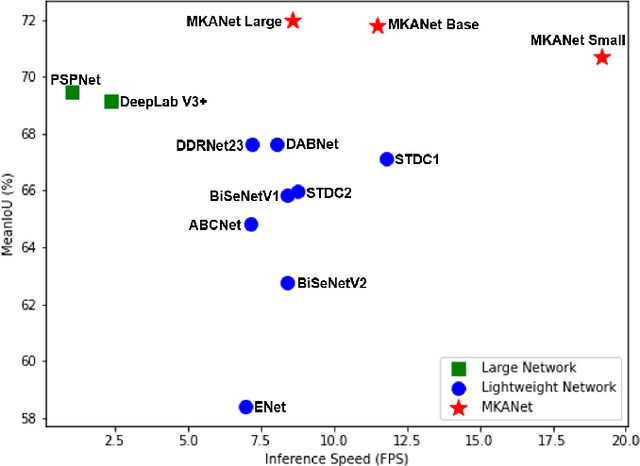


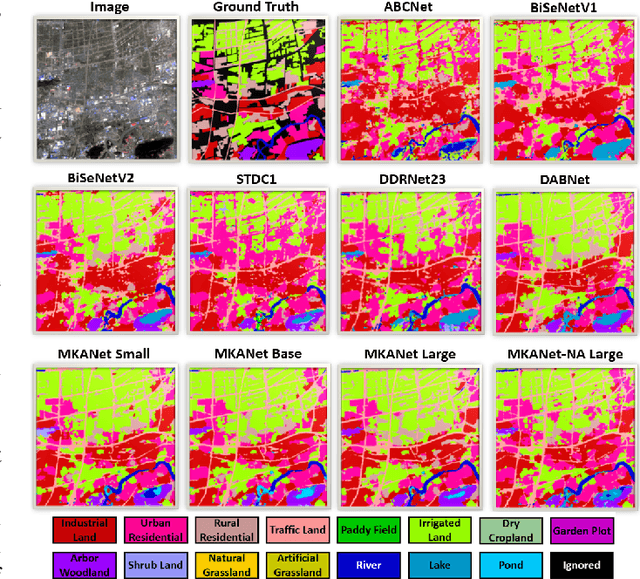
Land cover classification is a multi-class segmentation task to classify each pixel into a certain natural or man-made category of the earth surface, such as water, soil, natural vegetation, crops, and human infrastructure. Limited by hardware computational resources and memory capacity, most existing studies preprocessed original remote sensing images by down sampling or cropping them into small patches less than 512*512 pixels before sending them to a deep neural network. However, down sampling images incurs spatial detail loss, renders small segments hard to discriminate, and reverses the spatial resolution progress obtained by decades of years of efforts. Cropping images into small patches causes a loss of long-range context information, and restoring the predicted results to their original size brings extra latency. In response to the above weaknesses, we present an efficient lightweight semantic segmentation network termed MKANet. Aimed at the characteristics of top view high-resolution remote sensing imagery, MKANet utilizes sharing kernels to simultaneously and equally handle ground segments of inconsistent scales, and also employs parallel and shallow architecture to boost inference speed and friendly support image patches more than 10X larger. To enhance boundary and small segments discrimination, we also propose a method that captures category impurity areas, exploits boundary information and exerts an extra penalty on boundaries and small segment misjudgment. Both visual interpretations and quantitative metrics of extensive experiments demonstrate that MKANet acquires state-of-the-art accuracy on two land-cover classification datasets and infers 2X faster than other competitive lightweight networks. All these merits highlight the potential of MKANet in practical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge