MIN2Net: End-to-End Multi-Task Learning for Subject-Independent Motor Imagery EEG Classification
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2021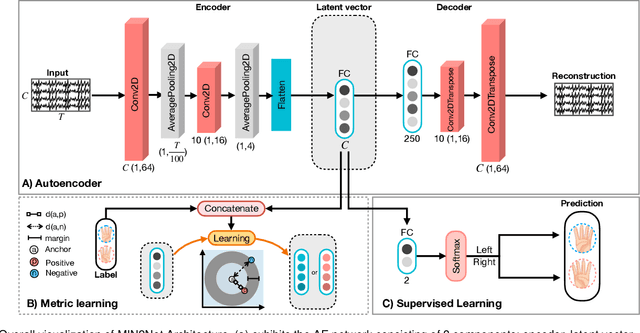
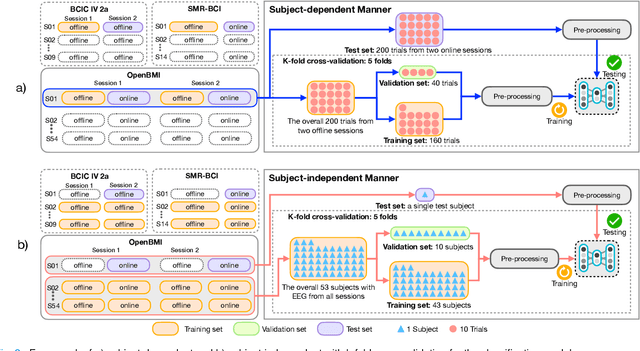
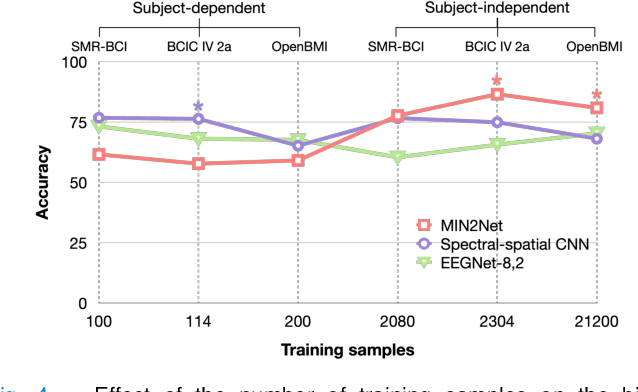
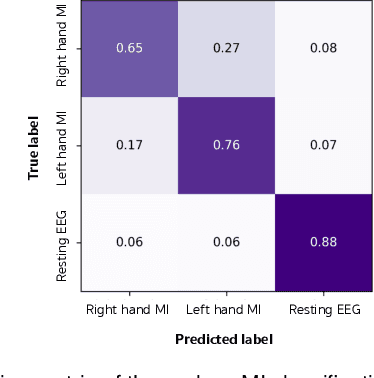
Advances in the motor imagery (MI)-based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) allow control of several applications by decoding neurophysiological phenomena, which are usually recorded by electroencephalography (EEG) using a non-invasive technique. Despite great advances in MI-based BCI, EEG rhythms are specific to a subject and various changes over time. These issues point to significant challenges to enhance the classification performance, especially in a subject-independent manner. To overcome these challenges, we propose MIN2Net, a novel end-to-end multi-task learning to tackle this task. We integrate deep metric learning into a multi-task autoencoder to learn a compact and discriminative latent representation from EEG and perform classification simultaneously. This approach reduces the complexity in pre-processing, results in significant performance improvement on EEG classification. Experimental results in a subject-independent manner show that MIN2Net outperforms the state-of-the-art techniques, achieving an accuracy improvement of 11.65%, 1.03%, and 10.53% on the BCI competition IV 2a, SMR-BCI, and OpenBMI datasets, respectively. We demonstrate that MIN2Net improves discriminative information in the latent representation. This study indicates the possibility and practicality of using this model to develop MI-based BCI applications for new users without the need for calibration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge