Micro-Behavior Encoding for Session-based Recommendation
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2022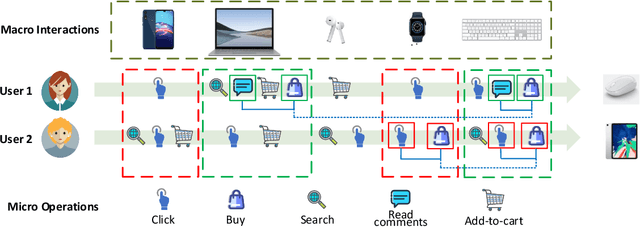
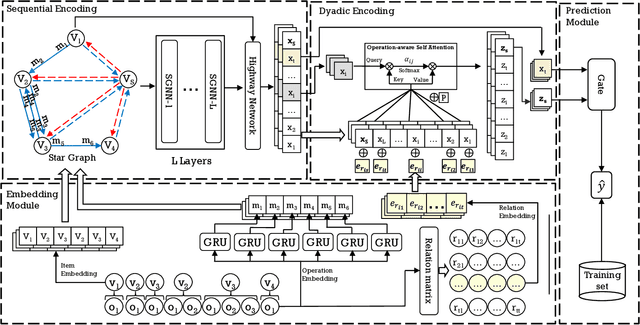
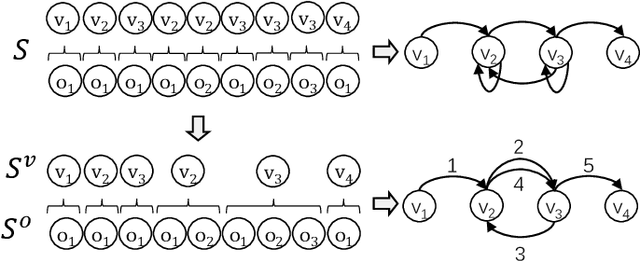
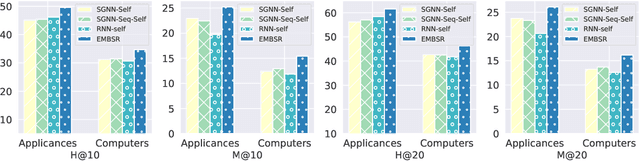
Session-based Recommendation (SR) aims to predict the next item for recommendation based on previously recorded sessions of user interaction. The majority of existing approaches to SR focus on modeling the transition patterns of items. In such models, the so-called micro-behaviors describing how the user locates an item and carries out various activities on it (e.g., click, add-to-cart, and read-comments), are simply ignored. A few recent studies have tried to incorporate the sequential patterns of micro-behaviors into SR models. However, those sequential models still cannot effectively capture all the inherent interdependencies between micro-behavior operations. In this work, we aim to investigate the effects of the micro-behavior information in SR systematically. Specifically, we identify two different patterns of micro-behaviors: "sequential patterns" and "dyadic relational patterns". To build a unified model of user micro-behaviors, we first devise a multigraph to aggregate the sequential patterns from different items via a graph neural network, and then utilize an extended self-attention network to exploit the pair-wise relational patterns of micro-behaviors. Extensive experiments on three public real-world datasets show the superiority of the proposed approach over the state-of-theart baselines and confirm the usefulness of these two different micro-behavior patterns for SR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge