Methods to Measure the Broncho-Arterial Ratio and Wall Thickness in the Right Lower Lobe for Defining Radiographic Reversibility of Bronchiectasis
Paper and Code
Jul 18, 2024


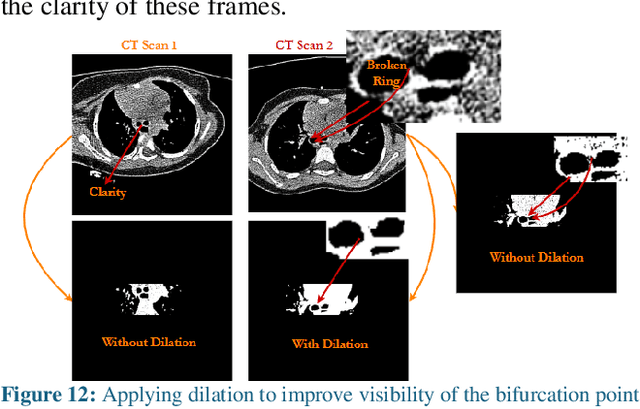
The diagnosis of bronchiectasis requires measuring abnormal bronchial dilation. It is confirmed using a chest CT scan, where the key feature is an increased broncho-arterial ratio (BAR) (>0.8 in children), often with bronchial wall thickening. Image processing methods facilitate quicker interpretation and detailed evaluations by lobes and segments. Challenges like inclined nature, oblique orientation, and partial volume effect make it difficult to obtain accurate measurements in the upper and middle lobes using the same algorithms. Therefore, accurate detection and measurement of airway and artery regions for BAR and wall thickness in each lobe require different image processing/machine learning methods. We propose methods for: 1. Separating the right lower lobe (RLL) region from full-length CT scans using the tracheal bifurcation (Carina) point as a central marker; 2. Locating the inner diameter of airways and outer diameter of arteries for BAR measurement; and 3. Measuring airway wall thickness (WT) by identifying the outer and inner diameters of airway boundaries. Analysis of 13 HRCT scans with varying thicknesses (0.67mm, 1mm, 2mm) shows the tracheal bifurcation frame can be detected accurately, with a deviation of +/- 2 frames in some cases. A Windows app was developed for measuring inner airway diameter, artery diameter, BAR, and wall thickness, allowing users to draw boundaries around visible BA pairs in the RLL region. Measurements of 10 BA pairs revealed accurate results comparable to those of a human reader, with deviations of +/- 0.10-0.15mm. Additional studies and validation are needed to consolidate inter- and intra-rater variability and enhance the methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge