Meta-Learning over Time for Destination Prediction Tasks
Paper and Code
Jun 29, 2022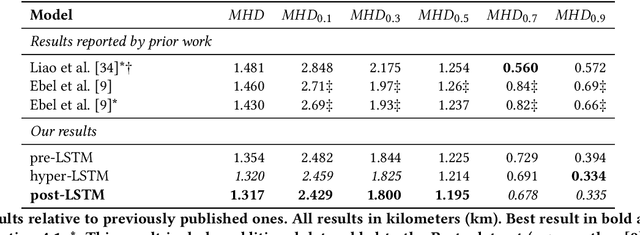
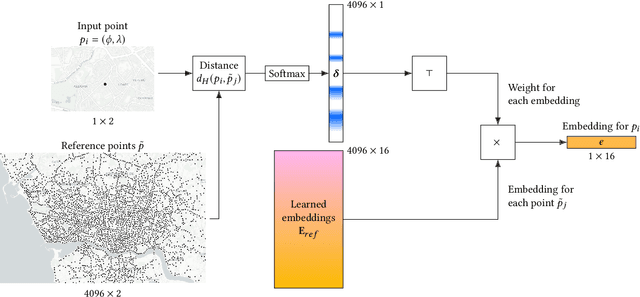
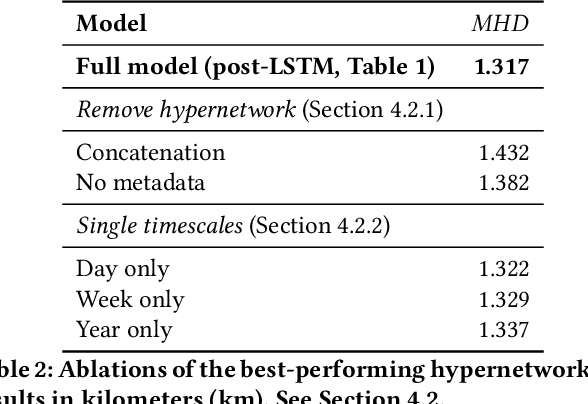
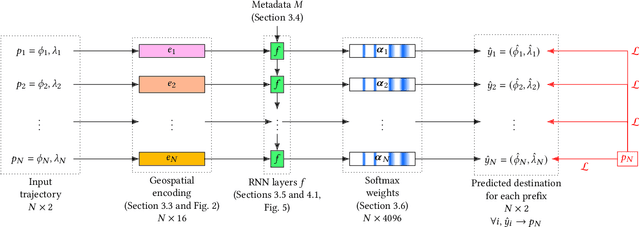
A need to understand and predict vehicles' behavior underlies both public and private goals in the transportation domain, including urban planning and management, ride-sharing services, and intelligent transportation systems. Individuals' preferences and intended destinations vary throughout the day, week, and year: for example, bars are most popular in the evenings, and beaches are most popular in the summer. Despite this principle, we note that recent studies on a popular benchmark dataset from Porto, Portugal have found, at best, only marginal improvements in predictive performance from incorporating temporal information. We propose an approach based on hypernetworks, a variant of meta-learning ("learning to learn") in which a neural network learns to change its own weights in response to an input. In our case, the weights responsible for destination prediction vary with the metadata, in particular the time, of the input trajectory. The time-conditioned weights notably improve the model's error relative to ablation studies and comparable prior work, and we confirm our hypothesis that knowledge of time should improve prediction of a vehicle's intended destination.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge