MedISure: Towards Assuring Machine Learning-based Medical Image Classifiers using Mixup Boundary Analysis
Paper and Code
Nov 23, 2023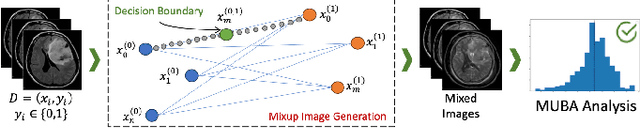
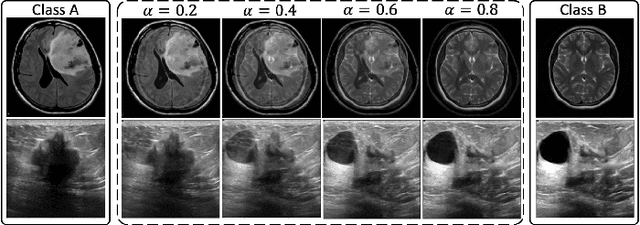
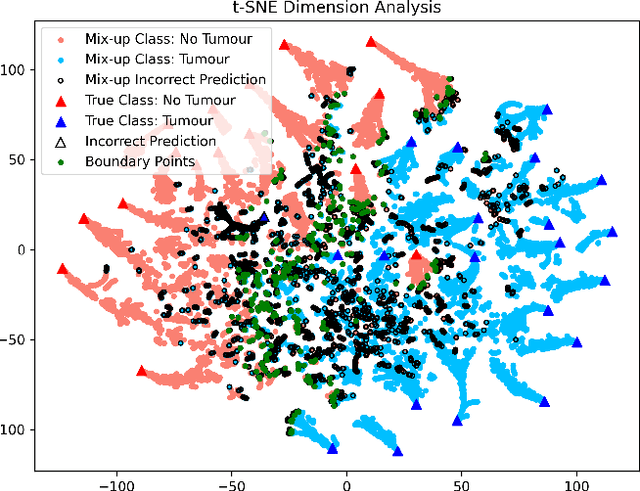
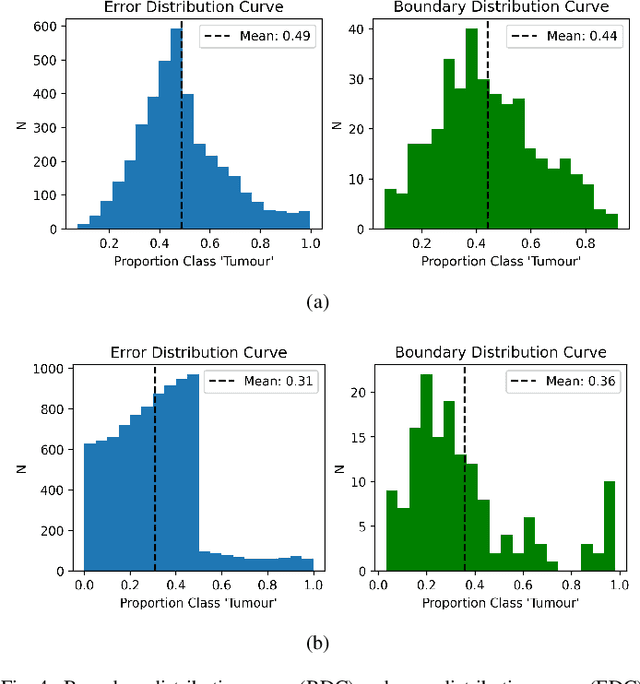
Machine learning (ML) models are becoming integral in healthcare technologies, presenting a critical need for formal assurance to validate their safety, fairness, robustness, and trustworthiness. These models are inherently prone to errors, potentially posing serious risks to patient health and could even cause irreparable harm. Traditional software assurance techniques rely on fixed code and do not directly apply to ML models since these algorithms are adaptable and learn from curated datasets through a training process. However, adapting established principles, such as boundary testing using synthetic test data can effectively bridge this gap. To this end, we present a novel technique called Mix-Up Boundary Analysis (MUBA) that facilitates evaluating image classifiers in terms of prediction fairness. We evaluated MUBA for two important medical imaging tasks -- brain tumour classification and breast cancer classification -- and achieved promising results. This research aims to showcase the importance of adapting traditional assurance principles for assessing ML models to enhance the safety and reliability of healthcare technologies. To facilitate future research, we plan to publicly release our code for MUBA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge