Measuring Fairness in Large-Scale Recommendation Systems with Missing Labels
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2024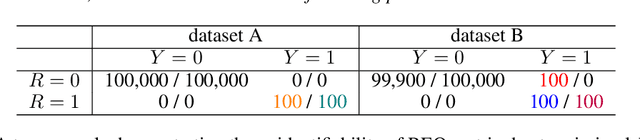

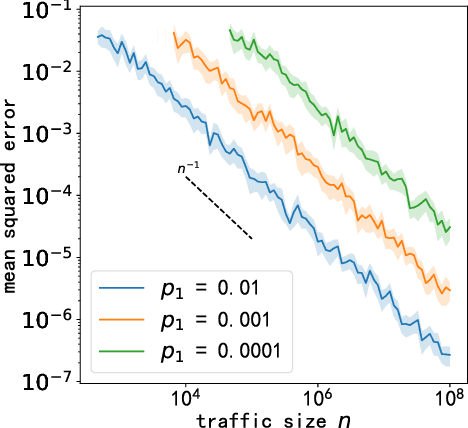
In large-scale recommendation systems, the vast array of items makes it infeasible to obtain accurate user preferences for each product, resulting in a common issue of missing labels. Typically, only items previously recommended to users have associated ground truth data. Although there is extensive research on fairness concerning fully observed user-item interactions, the challenge of fairness in scenarios with missing labels remains underexplored. Previous methods often treat these samples missing labels as negative, which can significantly deviate from the ground truth fairness metrics. Our study addresses this gap by proposing a novel method employing a small randomized traffic to estimate fairness metrics accurately. We present theoretical bounds for the estimation error of our fairness metric and support our findings with empirical evidence on real data. Our numerical experiments on synthetic and TikTok's real-world data validate our theory and show the efficiency and effectiveness of our novel methods. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to emphasize the necessity of random traffic in dataset collection for recommendation fairness, the first to publish a fairness-related dataset from TikTok and to provide reliable estimates of fairness metrics in the context of large-scale recommendation systems with missing labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge