Maximum Resilience of Artificial Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jul 05, 2017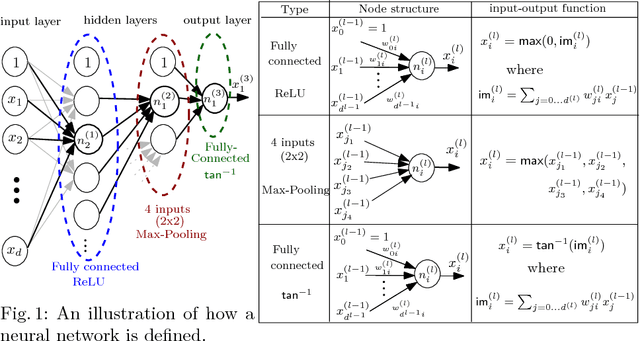
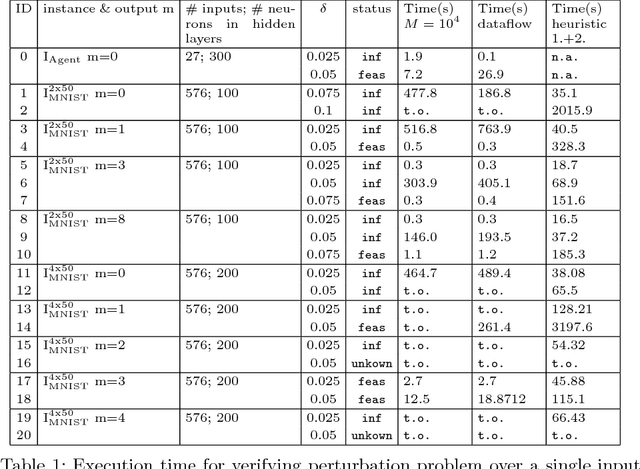
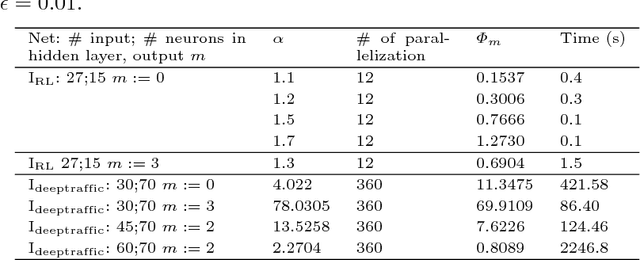
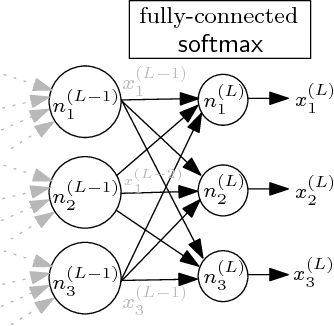
The deployment of Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) in safety-critical applications poses a number of new verification and certification challenges. In particular, for ANN-enabled self-driving vehicles it is important to establish properties about the resilience of ANNs to noisy or even maliciously manipulated sensory input. We are addressing these challenges by defining resilience properties of ANN-based classifiers as the maximal amount of input or sensor perturbation which is still tolerated. This problem of computing maximal perturbation bounds for ANNs is then reduced to solving mixed integer optimization problems (MIP). A number of MIP encoding heuristics are developed for drastically reducing MIP-solver runtimes, and using parallelization of MIP-solvers results in an almost linear speed-up in the number (up to a certain limit) of computing cores in our experiments. We demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of our approach by means of computing maximal resilience bounds for a number of ANN benchmark sets ranging from typical image recognition scenarios to the autonomous maneuvering of robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge