Max K-armed bandit: On the ExtremeHunter algorithm and beyond
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2017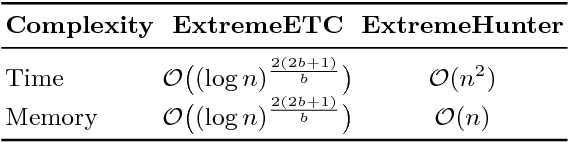
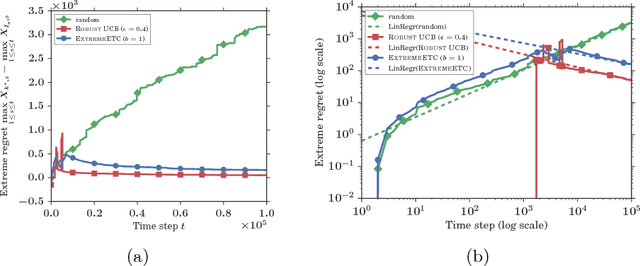
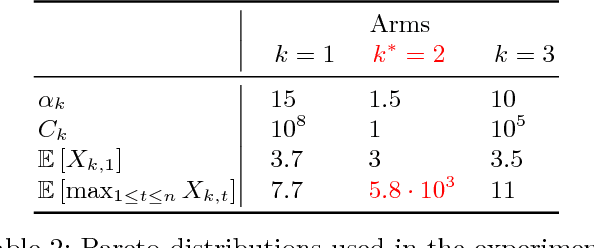
This paper is devoted to the study of the max K-armed bandit problem, which consists in sequentially allocating resources in order to detect extreme values. Our contribution is twofold. We first significantly refine the analysis of the ExtremeHunter algorithm carried out in Carpentier and Valko (2014), and next propose an alternative approach, showing that, remarkably, Extreme Bandits can be reduced to a classical version of the bandit problem to a certain extent. Beyond the formal analysis, these two approaches are compared through numerical experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge