Mask-based Membership Inference Attacks for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2024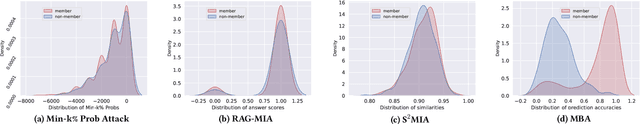
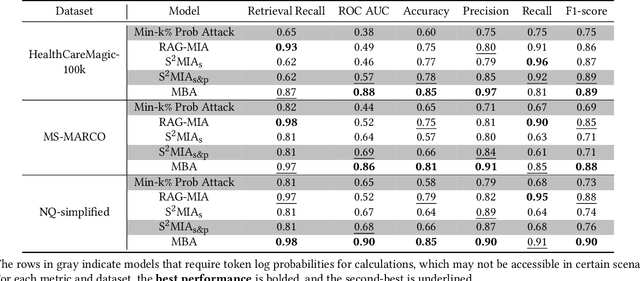
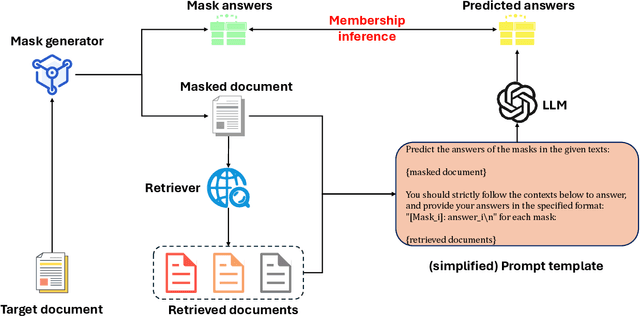
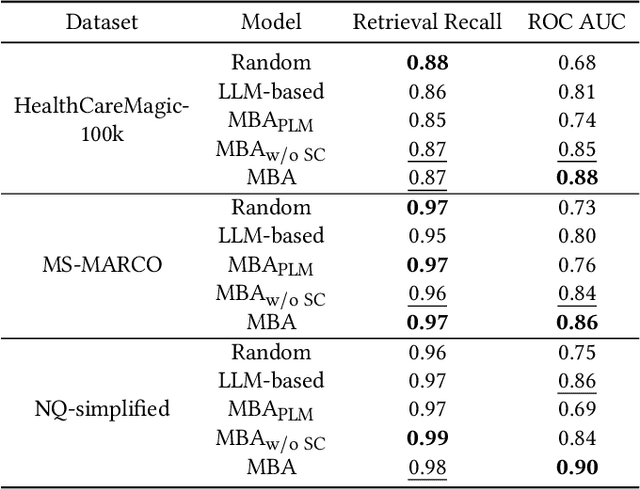
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has been an effective approach to mitigate hallucinations in large language models (LLMs) by incorporating up-to-date and domain-specific knowledge. Recently, there has been a trend of storing up-to-date or copyrighted data in RAG knowledge databases instead of using it for LLM training. This practice has raised concerns about Membership Inference Attacks (MIAs), which aim to detect if a specific target document is stored in the RAG system's knowledge database so as to protect the rights of data producers. While research has focused on enhancing the trustworthiness of RAG systems, existing MIAs for RAG systems remain largely insufficient. Previous work either relies solely on the RAG system's judgment or is easily influenced by other documents or the LLM's internal knowledge, which is unreliable and lacks explainability. To address these limitations, we propose a Mask-Based Membership Inference Attacks (MBA) framework. Our framework first employs a masking algorithm that effectively masks a certain number of words in the target document. The masked text is then used to prompt the RAG system, and the RAG system is required to predict the mask values. If the target document appears in the knowledge database, the masked text will retrieve the complete target document as context, allowing for accurate mask prediction. Finally, we adopt a simple yet effective threshold-based method to infer the membership of target document by analyzing the accuracy of mask prediction. Our mask-based approach is more document-specific, making the RAG system's generation less susceptible to distractions from other documents or the LLM's internal knowledge. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach compared to existing baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge